Studio Clustering 
Crafter Studio can be clustered for high-availability.
Here’s an overview of a serverless Studio Enterprise cluster:
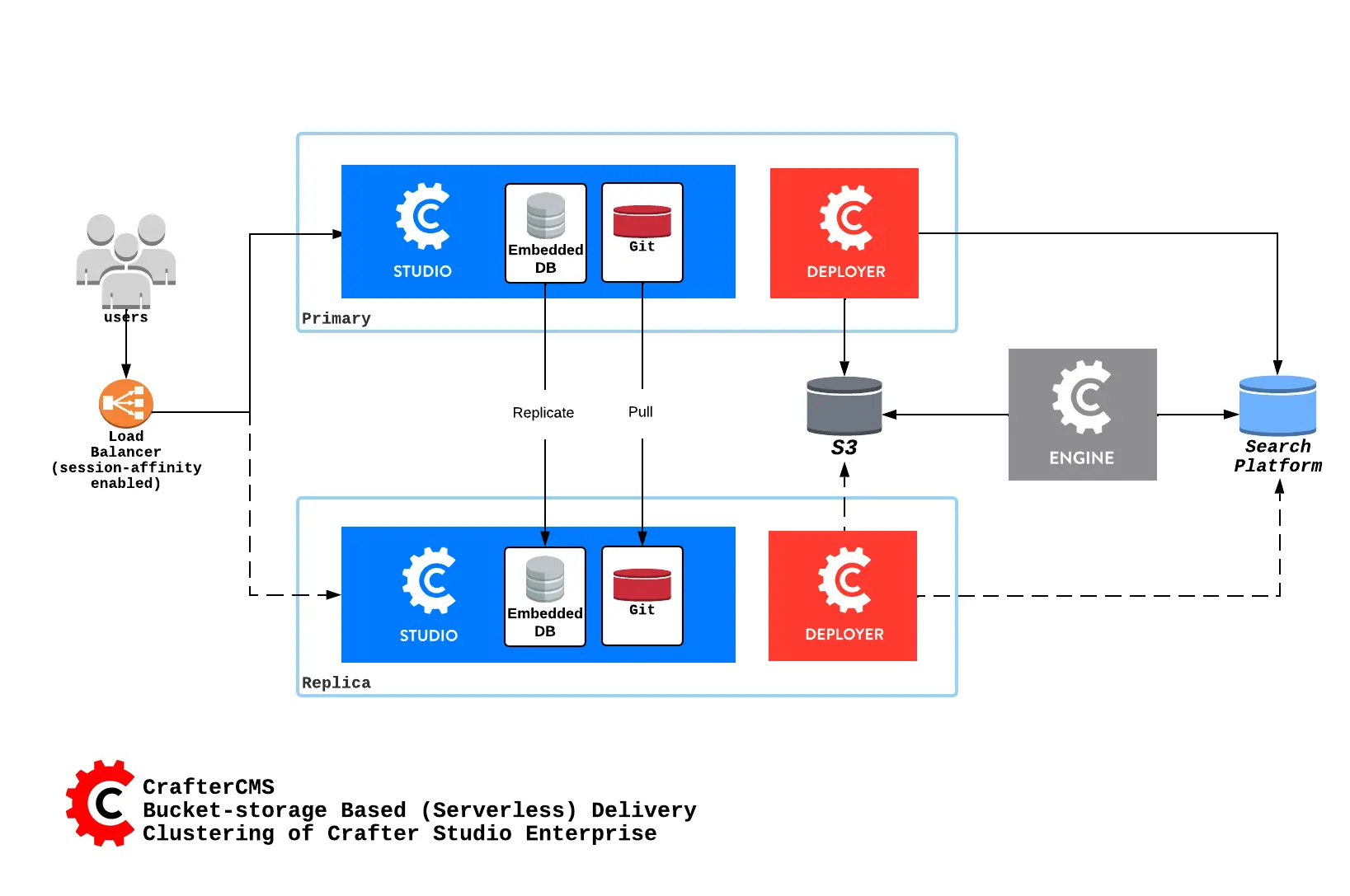
Here’s an overview of a disk-based Studio Enterprise cluster:
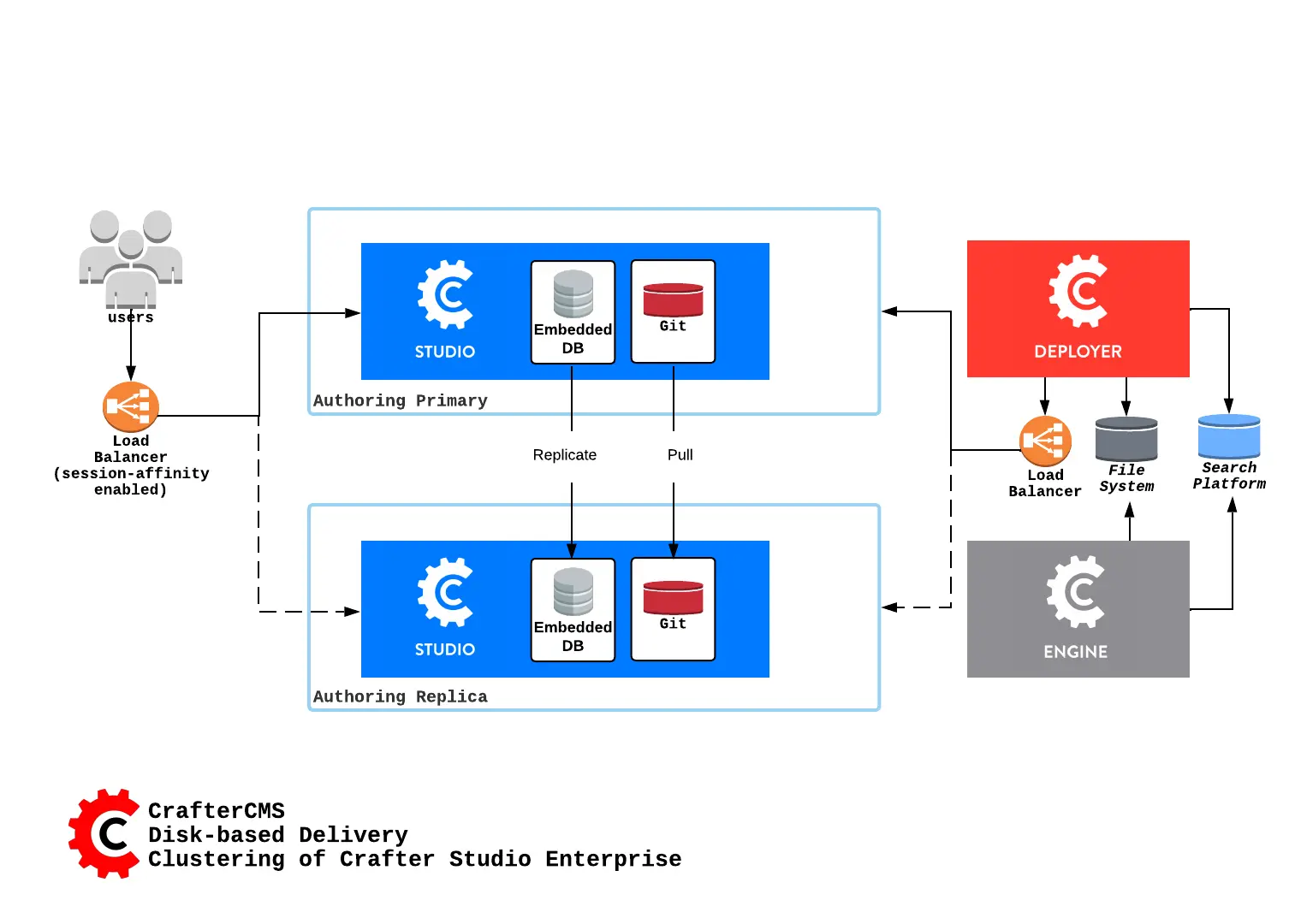
A node is a server running an instance of Crafter Studio and a cluster consists of two or more nodes. In the image above, two Crafter Studio instances are clustered as primary and replica.
When setting up a Studio cluster, a specific node needs to be started first as a reference point, then the other node/s can join and form the cluster. This is known as cluster bootstrapping. Bootstrapping is the first step to introduce a node as Primary Component, which others will see as a reference point to sync up with.
The Primary Component is a central concept on how to ensure that there is no opportunity for database inconsistency or divergence between the nodes in case of a network split. The Primary Component is a set of nodes that communicate with each other over the network and contains the majority of the nodes. There’s no Primary Component yet when starting up a cluster, hence the need of the first node to bootstrap the Component. The other nodes will then look for the existing Primary Component to join.
Note
Studio nodes use an in-memory distributed data store to orchestrate the bootstrapping of the Primary Component, so you don’t need to do it. When the cluster is started, the nodes synchronize through the data store to decide which one does the bootstrapping, and then the rest join the Primary Component.
Once the cluster is up, one node in the cluster is elected to be the primary and the rest of the node(s) as replica(s). Deployment processors can be configured when Studio Clustering is setup.
Requirements
Before we begin configuring Studio for clustering, the following must be setup:
A load balancer or DNS server directing traffic to the primary node, and can failover to the replica node if the primary is not healthy
Configuration
We’ll take a look at an example of how to setup a two node cluster with Studio step by step here. Afterwards, you can then take a look at an example of setting up Studio clustering using a Kubernetes deployment
Setup a Two Node Cluster with Studio
In this section, we’ll look at an example of how to setup a two node cluster with Studio.
To setup a two node cluster with Studio we’ll need to do the following:
Configure Nodes in the Cluster
Start the Nodes in the Cluster
Requirements
At least 2 servers running Linux (Remember that Studio’s cluster runs only in Linux) with the following ports open:
8080for http33306for the DB5701for hazelcast
Enterprise version of CrafterCMS
Studio’s clustering requires the
libssl1.0.0(orlibssl1.0.2) shared library. Some Linux distros does not come with the library pre-installed and may need to be installed.
Configuring Nodes in the Cluster
Install the Enterprise version of CrafterCMS on all the nodes
Configure the Git repository clustering for all nodes by configuring the following settings in the
studio-config-override.yamlfile.bin/apache-tomcat/shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/studio-config-override.yaml################################################## ## Clustering ## ################################################## # ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # IMPORTANT: To enable clustering, please specify the following Spring profile # in your crafter-setenv.sh: # - SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=crafter.studio.dbClusterPrimaryReplica # You will need to uncomment the Hazelcast and Studio DB Cluster property sections too # ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Cluster Git URL format for synching members. # - Typical SSH URL format: ssh://{username}@{localAddress}{absolutePath} # - Typical HTTPS URL format: https://{localAddress}/repos/sites studio.clustering.sync.urlFormat: ssh://{username}@{localAddress}{absolutePath} # Notifications #studio.notification.cluster.startupError.subject: "Action Required: Studio Cluster Error" #studio.notification.cluster.startupError.template: startupError.ftl #studio.notification.cluster.startupError.recipients: admin@example.com # Cluster member registration, this registers *this* server into the pool # Cluster node registration data, remember to uncomment the next line studio.clustering.node.registration: # This server's local address (reachable to other cluster members). You can also specify a different port by # attaching :PORT to the address (e.g. 192.168.1.200:2222) # localAddress: ${env:CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS} # Authentication type to access this server's local repository # possible values # - none (no authentication needed) # - basic (username/password authentication) # - key (ssh authentication) authenticationType: none # Username to access this server's local repository # username: user # Password to access this server's local repository # password: SuperSecurePassword # Private key to access this server's local repository (multiline string) # privateKey: | # -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- # privateKey # -----END PRIVATE KEY-----
Uncomment and leave the value of studio.clustering.node.registration.localAddress as
${env:CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS}(you will configure the node address in a later step), then configure the repository authentication:studio.clustering.node.registration.authenticationType: authentication type to access this server’s local repository
studio.clustering.node.registration.username: username to access this server’s local repository
studio.clustering.node.registration.password: password to access this server’s local repository
studio.clustering.node.registration.privateKey: private key to access this server’s local repository (multiline string) when using
keyas authentication type to access this server’s local repository
Note
You can use the node’s default SSH keys, located in
~/.ssh/id_rsaand~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub, if you set theauthenticationTypetonone. You can also use~/.ssh/configif you need to configure certain aspects of SSH authentication, likeStrictHostKeyChecking. For example, you can disableStrictHostKeyCheckingfor hostnames with*.hostnamespaceso that you don’t need to validate the SSH host keys before running Studio:Host *.hostnamespace StrictHostKeyChecking nostudio.notification.cluster.startupError.subject: subject for the email
studio.notification.cluster.startupError.template: template used for the email message
studio.notification.cluster.startupError.recipients: list of emails to send the notification, must be separated by commas.
Configure the Hazelcast configuration file location in Studio, by uncommenting
studio.hazelcast.config.location. You will create the Hazelcast configuration file in a later step.bin/apache-tomcat/shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/studio-config-override.yaml################################################## ## Hazelcast ## ################################################## # Location of the Hazelcast config path (must be in YAML format) studio.hazelcast.config.location: classpath:crafter/studio/extension/hazelcast-config.yaml
Configure the following times and locations. Leave the environment variables, e.g.
${env:MARIADB_CLUSTER_NAME}. You can see the configuration of the environment variables in a later step.bin/apache-tomcat/shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/studio-config-override.yaml################################################## ## Studio DB Cluster ## ################################################## # DB cluster name studio.db.cluster.name: ${env:MARIADB_CLUSTER_NAME} # Count for the number of Studio cluster members studio.db.cluster.nodes.count: ${env:MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_COUNT} # DB cluster address of the local node (which will be seen by other members of the cluster) studio.db.cluster.nodes.local.address: ${env:MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS} # DB cluster name of the local node (which will be seen by other members of the cluster) studio.db.cluster.nodes.local.name: ${env:MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_NAME} # Time in seconds when each Studio member of the DB cluster should report its status studio.db.cluster.nodes.status.report.period: 30 # Time in seconds when each report of a DB member should expire (needs to be higher than the report period) studio.db.cluster.nodes.status.report.ttl: 60 # Time in seconds before giving up on waiting for all cluster members to appear online on startup studio.db.cluster.nodes.startup.wait.timeout: 300 #Time in seconds before giving up on waiting for cluster bootstrap to complete (at least a node is active, # which means the node is synced AND its Studio has finished starting up) studio.db.cluster.bootstrap.wait.timeout: 180
Configure the environment variables for the nodes in the
crafter-setenv.shfile.bin/crafter-setenv.sh# Uncomment to enable clustering export SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=crafter.studio.dbClusterPrimaryReplica ... # -------------------- Cluster variables ------------------- export CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS=${CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS:="$(hostname -i)"} # -------------------- MariaDB Cluster variables -------------------- export MARIADB_CLUSTER_NAME=${MARIADB_CLUSTER_NAME:="studio_db_cluster"} export MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_COUNT=${MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_COUNT:="2"} export MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS=${MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS:="$(hostname -i)"} export MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_NAME=${MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_NAME:="$(hostname)"} # Uncomment to enable primary/replica clustering # CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_SERVER_ID must have different value across cluster nodes. Value is numeric with range 1 to 4294967295 IP="$CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS" OCTET_0=`expr match "$IP" '\([0-9]\+\)\..*'` OCTET_1=`expr match "$IP" '[0-9]\+\.\([0-9]\+\)\..*'` OCTET_2=`expr match "$IP" '[0-9]\+\.[0-9]\+\.\([0-9]\+\)\..*'` OCTET_3=`expr match "$IP" '[0-9]\+\.[0-9]\+\.[0-9]\+\.\([0-9]\+\)'` BIN=$(($((OCTET_0 * $((256**3))))+$((OCTET_1 * $((256**2))))+$((OCTET_2 * 256))+$((OCTET_3 * 1)))) # CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_SERVER_ID must have different value across cluster nodes. Value is numeric with range 1 to 4294967295 export CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_SERVER_ID=${CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_SERVER_ID:="$BIN"} # Cluster bin log base name for primary replica replication export CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_LOG_BASENAME=${CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_LOG_BASENAME:="crafter_cluster"} # Cluster wait interval for replica to be ready on startup export CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_REPLICA_READY_WAIT_INTERVAL=${CRAFTER_DB_CLUSTER_REPLICA_READY_WAIT_INTERVAL:="30000"} # Database replication user export MARIADB_REPLICATION_USER=${MARIADB_REPLICATION_USER:="crafter_replication"} # Database replication password export MARIADB_REPLICATION_PASSWD=${MARIADB_REPLICATION_PASSWD:="crafter_replication"}
where:
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE: with the value
crafter.studio.dbClusterPrimaryReplica, enables primary/replica clusteringCLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS: hostname or IP of the local node to be registered in the Git repository cluster, should be reachable to other cluster members.
MARIADB_CLUSTER_NAME: name of the MariaDB cluster.
MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_COUNT: the number of Studio nodes in the cluster.
MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_ADDRESS: hostname of IP of the local node to be registered to the MariaDB cluster, should be reachable to other cluster members.
MARIADB_CLUSTER_NODE_NAME: name of cluster node to be registered to the MariaDB cluster.
Create a Hazelcast configuration file in
shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/hazelcast-config.yaml.Studio uses Hazelcast as the in-memory distributed data store to orchestrate the bootstrapping of the MariaDB cluster. You can find more about Hazelcast in https://hazelcast.org/ and its configuration in https://docs.hazelcast.org/docs/latest/manual/html-single/#understanding-configuration. In this configuration file you specify the way the nodes discover each other in the Hazelcast cluster.
We recommend you create a simple configuration in each node with the list of addresses of the cluster nodes:
bin/apache-tomcat/shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/hazelcast-config.yamlhazelcast: network: join: multicast: enabled: false tcp-ip: enabled: true member-list: - 192.168.56.1 - 192.168.56.114
If using Kubernetes, Studio also supports configuration through the Kubernetes Hazelcast Plugin:
bin/apache-tomcat/shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/hazelcast-config.yamlhazelcast: network: join: multicast: enabled: false kubernetes: enabled: true namespace: default service-name: authoring-service-headless resolve-not-ready-addresses: true
Note
Please apply the
rbac.yamlmentioned in the Kubernetes Hazelcast Plugin documentation in your Kubernetes cluster, before even starting any Studio pods.
Starting the Nodes in the Cluster
After finishing the node configurations, we are now ready to start the cluster. Please start the cluster nodes
in close succession, one after the other. If you take more than 5 minutes to start all the cluster nodes then
the nodes already running will timeout while trying to synchronize for bootstrapping (you can configure this
timeout in the bin/apache-tomcat/shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/studio-config-override.yaml file,
under the property studio.db.cluster.nodes.startup.wait.timeout).
Configuring the Deployer for Studio Clustering
Since 4.1.1The deployer is cluster aware and is able to run deployment processors based on the value set in the deployment processor property runInClusterMode (described here) and the value returned by the Studio clusterMode API.
The runInClusterMode property can be configured for any processor in the deployer target context xml, e.g:
...
<bean id="gitDiffProcessor" parent="deploymentProcessor"
class="org.craftercms.deployer.impl.processors.git.GitDiffProcessor">
<property name="localRepoFolder" value="${target.localRepoPath}"/>
<property name="blobFileExtension" value="${deployer.main.targets.config.blob.file.extension}"/>
<property name="processedCommitsStore" ref="processedCommitsStore"/>
<property name="runInClusterMode" value="ALWAYS" />
</bean>
Or in the target yaml configuration:
...
- processorName: searchIndexingProcessor
excludeFiles: ['^/sources/.*$']
runInClusterMode: "ALWAYS"
Remember that the clusterMode API needs the studioManagementToken configured in the target like below:
target:
...
...
studioUrl: http://localhost:8080/studio
studioManagementToken: ${deployer.main.management.studioAuthorizationToken}
...
...
The deployment processor configured above runs whenever the clusterMode returned is not UNKNOWN and meets one of the following conditions:
runInClusterModeis set toALWAYSrunInClusterModevalue matches the currentclusterMode
Failover
Studio clustering is based on Primary/Replica clustering mechanics. Failure scenarios:
Replica node(s) failure: In case of one or more replicas failing, the cluster will continue to work normally. New replicas can join and catch up.
Primary node failure: In case of the primary node failing, the load balancer or DNS must either automatically or manually redirect or repoint traffic to the next healthy node.
The replicas will automatically perform an election and appoint a new primary. The new primary’s health check will report that it’s ready to receive traffic, the load balancer or DNS can then redirect or repoint traffic to the new primary.
As a new node or the old failed primary rejoin the cluster, they’ll assume a replica role and catch up with the new primary.
Crafter Studio provides a health check endpoint at /studio/api/2/monitoring/status?token={your management token}. You can use this endpoint to check the health of any node in the cluster. This can be used to facilitate automatic failover.
Multi-Region Considerations
For clusters with nodes in multi-regions utilizing S3 buckets, AWS provides solutions for handling multi-region deployments of S3 buckets.
AWS supports access points for managing access to a shared bucket on S3. For more information on Amazon S3 Access Points, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/access-points.html
For clusters with S3 buckets located in multiple AWS regions, Amazon S3 Multi-Region Access Points provide a global endpoint that applications can use to fulfill requests from. For more information on Multi-Region Access Points in Amazon S3, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/MultiRegionAccessPoints.html
AWS S3 also supports bucket replication (S3 replication) irrespective of the region they belong to, which provides data protection against disasters, minimizing latency, etc. For more information on S3 bucket replication for use with multi-region access points, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/MultiRegionAccessPointBucketReplication.html
Here’s some more information on S3 replication: https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/whats-new/2020/12/amazon-s3-replication-adds-support-two-way-replication/
Backup and Restore
CrafterCMS comes with a script to backup and restore your environment, as described here
There are a couple of ways to backup and restore your cluster:
Shutdown the cluster first then back up the Primary and the Replicas and restore both nodes when necessary
Shutdown the cluster first then backup and restore only 1 node (Primary or Replica), which will become Primary. You then have to add a Replica using the instructions here.
Troubleshooting
Check if the Cluster is Running
There are a few ways to check that the cluster is running.
via logs
via the status
via the Global Transaction ID
Via Logs
To check that the cluster is up, you can inspect the $CRAFTER_HOME/logs/tomcat/catalina.out of the nodes for
the following entries:
Primary starting up (one of the nodes):
[INFO] 2022-01-28T18:07:54,009 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | Synchronizing startup of node 192.168.56.1 with DB cluster 'studio_db_cluster' 28-Jan-2022 18:07:54.016 INFO [main] com.hazelcast.internal.partition.impl.PartitionStateManager.null [192.168.56.1]:5701 [dev] [4.2.4] Initializing cluster partition table arrangement... [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:07:54,178 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | Waiting for initial report of all 2 DB cluster members... ... [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:24,237 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | Waiting for initial report of all 2 DB cluster members... [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:54,241 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | All 2 DB cluster members have started up [ERROR] 2022-01-28T18:08:54,242 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | DbPrimaryReplicaClusterMember {address='192.168.56.1', port='33306', name='192.168.56.1', status='null', timestamp=1643389674007, primary=false, file='null', position=0, replica=false, ioRunning='null', sqlRunning='null', secondsBehindMaster=9223372036854775807} [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:54,251 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | Local DB cluster node will start primary. [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:54,252 [main] [mariadb4j.DB] | Starting up the database...Rest of the nodes:
[INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:28,078 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | Synchronizing startup of node 192.168.56.114 with DB cluster 'studio_db_cluster' [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:28,153 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | Waiting for initial report of all 2 DB cluster members... [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:58,167 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | All 2 DB cluster members have started up [ERROR] 2022-01-28T18:08:58,169 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | DbPrimaryReplicaClusterMember {address='192.168.56.114', port='33306', name='192.168.56.114', status='null', timestamp=1643389708075, primary=false, file='null', position=0, replica=false, ioRunning='null', sqlRunning='null', secondsBehindMaster=9223372036854775807} [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:08:58,183 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | Waiting for primary to start... [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:09:28,195 [main] [cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl] | primary started [INFO] 2022-01-28T18:09:28,202 [main] [mariadb4j.DB] | Starting up the database...
Via the Status
You can also check that the cluster is working by logging into MariaDB with the mysql client from the
primary or the replica and checking the status:
From the command line in the server, go to
$CRAFTER_HOME/bin/dbms/binand run themysqlprogram./mysql -S /tmp/MariaDB4j.33306.sock
Inside the MySQL client, run the following:
Primary:
SHOW MASTER STATUS\GMariaDB [crafter]> SHOW MASTER STATUS\G *************************** 1. row *************************** File: crafter_cluster-bin.000001 Position: 2812853 Binlog_Do_DB: Binlog_Ignore_DB: 1 row in set (0.000 sec)Replica:
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\GMariaDB [crafter]> SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G [42/1943] *************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event Master_Host: 172.31.70.118 Master_User: crafter_replication Master_Port: 33306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: crafter_cluster-bin.000001 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 2776943 Relay_Log_File: crafter_cluster-relay-bin.000004 Relay_Log_Pos: 656828 Relay_Master_Log_File: crafter_cluster-bin.000001 Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes ..... ........
Via the Global Transaction ID
On a primary server, all database updates are written into the binary log as binlog events. A replica server
connects to the primary and reads the binlog events, then applies the events locally to replicate
the changes in the primary. For each event group (transaction) in the binlog, a unique id is attached
to it, called the Global Transaction ID or GTID.
To check our cluster, we can check the gtid_current_pos system variable in the primary and
the gtid_slave_pos system variable in the replica.
The gtid_current_pos system variable contains the GTID of the last transaction applied to the database
for each replication domain. The value is read-only, but it is updated whenever a transaction is written
to the binary log and/or replicated by a replica thread, and that transaction’s GTID is considered newer
than the current GTID for that domain.
The gtid_slave_pos system variable contains the GTID of the last transaction applied to the database by the server’s replica threads for each replication domain. This system variable’s value is automatically updated whenever a replica thread applies an event group.
To learn more about the global transaction ID, see https://mariadb.com/kb/en/gtid/
To check the gtid_current_pos and gtid_slave_pos system variables, log into MariaDB with the
mysql client from the primary or the replica:
From the command line in the server, go to
$CRAFTER_HOME/bin/dbms/binand run themysqlprogram./mysql -S /tmp/MariaDB4j.33306.sock
Inside the MySQL client, run the following:
Primary:
SELECT @@GLOBAL.gtid_current_pos;MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT @@GLOBAL.gtid_current_pos; +---------------------------+ | @@GLOBAL.gtid_current_pos | +---------------------------+ | 0-167772164-2132 | +---------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
Replica:
SELECT @@GLOBAL.gtid_slave_pos;MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT @@GLOBAL.gtid_slave_pos; +-------------------------+ | @@GLOBAL.gtid_slave_pos | +-------------------------+ | 0-167772164-2145 | +-------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
Git/DB Sync Failure
Whenever your authoring cluster has a Git or DB sync failure, the following logs may appear:
[ERROR] 2022-10-19T17:22:24,358 [main] [validation.ReplicaNodeRepositoryCheck] | Branch 'master' in repository '/opt/crafter/cluster/crafter/data/repos/sites/ed123/sandbox/.git' has commits ahead of the primary node at '172.31.70.118'
[ERROR] 2022-10-19T17:22:24,359 [main] [validation.NodeStateCheckerImpl] | Failed to start Crafter Studio cluster node due to start-up conflicts. Please review the logs and resolve the conflicts.
[ERROR] 2022-10-19T17:22:24,598 [main] [cluster.StudioClusterUtils] | Error notification email has been sent
...
Caused by: org.craftercms.studio.api.v2.exception.DbClusterStartupException: Failed to start DB replica: Error 'Duplicate entry '4' for key 'PRIMARY'' on query. Default database: 'crafter'. Query: 'INSERT INTO audit (organization_id, site_id, operation, operation_timestamp, origin, primary_target_id,
primary_target_type, primary_target_subtype, primary_target_value, actor_id, actor_details, cluster_node_id)
VALUES (1, 1, 'LOGIN', IFNULL(NULL, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP), 'API',
'admin', 'User', NULL, 'admin', 'admin',
NULL, '172.31.70.118')'
at org.craftercms.studio.impl.v2.dal.cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl.checkForErrors(DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl.java:598) ~[classes/:4.0.2-SNAPSHOT]
at org.craftercms.studio.impl.v2.dal.cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl.waitForLocalReplicaToSync(DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl.java:571) ~[classes/:4.0.2-SNAPSHOT]
at org.craftercms.studio.impl.v2.dal.cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl.synchronizeStartup(DbPrimaryReplicaClusterSynchronizationServiceImpl.java:270) ~[classes/:4.0.2-SNAPSHOT]
at org.craftercms.studio.impl.v2.dal.cluster.DbPrimaryReplicaClusterAwareMariaDB4jSpringService.start(DbPrimaryReplicaClusterAwareMariaDB4jSpringService.java:51) ~[classes/:4.0.2-SNAPSHOT]
at ch.vorburger.mariadb4j.MariaDB4jService.postConstruct(MariaDB4jService.java:64) ~[mariaDB4j-core-2.5.3.jar:?]
at jdk.internal.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) ~[?:?]
...
An email will also be sent to the configured list of recipients to inform them of the failure.
See the Setup a Two Node Cluster with Studio article then scroll to the failure notification properties section for more information on how to configure the list of recipients to be informed in case of a startup failure in the authoring cluster.
This section discusses how to fix the sync failure in your authoring cluster.
Fixing the Sync Failure
The first thing to do when a sync failure happens is to figure out whether the sync failure is in the DB or Git. The email sent to configured recipients when the sync failure happened will indicate whether it’s a DB or a Git sync failure. From the logs, you can also determine if it was a DB or a Git sync failure.
DB sync failure
For a DB sync failure, the logs will contain a message like below:
...
Failed to start DB replica:
...
as seen above and the following email will be sent if configured:
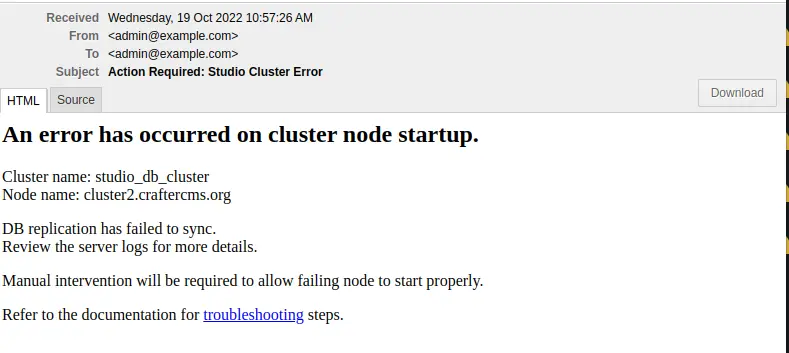
Before performing any valid intervention on the database, it will need to be started first, then the user needs to login.
The first thing that needs to be done is to start the database. To start the database, run the following:
CRAFTER_HOME/bin/dbms/bin/mysqld --no-defaults --console --basedir=CRAFTER_HOME/bin/dbms --datadir=CRAFTER_HOME/data/db --port=33306 --socket=/tmp/MariaDB4j.33306.sock --max_allowed_packet=128M --max-connections=500
This is the output when running the command above:
/opt/crafter/bin/dbms/bin/mysqld --no-defaults --console --basedir=/opt/crafter/bin/dbms --datadir=/opt/crafter/data/db --port=33306 --socket=/tmp/MariaDB4j.33306.sock --max_allowed_packet=128M --max-connections=500 2022-10-20 19:49:22 0 [Note] ./mysqld (mysqld 10.4.20-MariaDB) starting as process 8862 ... 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Using Linux native AIO 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Mutexes and rw_locks use GCC atomic builtins 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Uses event mutexes 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Compressed tables use zlib 1.2.11 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Number of pools: 1 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Using SSE2 crc32 instructions 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Initializing buffer pool, total size = 128M, instances = 1, chunk size = 128M 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Completed initialization of buffer pool 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: If the mysqld execution user is authorized, page cleaner thread priority can be changed. See the man page of setpriority(). 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: 128 out of 128 rollback segments are active. 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Creating shared tablespace for temporary tables 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Setting file './ibtmp1' size to 12 MB. Physically writing the file full; Please wait ... 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: File './ibtmp1' size is now 12 MB. 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Waiting for purge to start 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: 10.4.20 started; log sequence number 1389822; transaction id 407 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Loading buffer pool(s) from /opt/crafter/data/db/ib_buffer_pool 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] Plugin 'FEEDBACK' is disabled. 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] Server socket created on IP: '::'. 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] InnoDB: Buffer pool(s) load completed at 221020 19:49:23 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] Reading of all Master_info entries succeeded 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] Added new Master_info '' to hash table 2022-10-20 19:49:23 0 [Note] ./mysqld: ready for connections. Version: '10.4.20-MariaDB' socket: '/tmp/MariaDB4j.33306.sock' port: 33306 MariaDB Server
Login to the database by running the following command then entering the database root password:
CRAFTER_HOME/bin/dbms/bin/mysql -u <db_root_user> -p --socket=/tmp/MariaDB4j.33306.sock
The <db_root_user> by default is
rootwith password set torootor empty. Remember to replace <db_root_user> with the actualrootuser (MARIADB_ROOT_USER) value and enter the actual password (MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWD) value used in your system, which can be found in thecrafter-setenv.shfile under theCRAFTER_HOME/binfolder.In the sample run below, the default root user
rootis used and the corresponding password:./mysql -u root -p --socket=/tmp/MariaDB4j.33306.sock Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 8 Server version: 10.4.20-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]>
The intervention on the database may now be performed once the admin is logged in to the database. After performing the fix, stop the database then restart the node.
If an admin reviews the node states and thinks everything is fine but still receives DB sync errors, the admin may decide if MariaDB should ignore those errors and continue. To ignore the errors, a manual intervention is required and may be done by following the instructions here
Git sync failure
For a Git sync failure, the logs will contain a message like below:
...
Branch 'master' in repository '/opt/crafter/data/repos/sites/ed123/sandbox/.git' has commits ahead of the primary node
...
as seen above and the following email will be sent if configured:
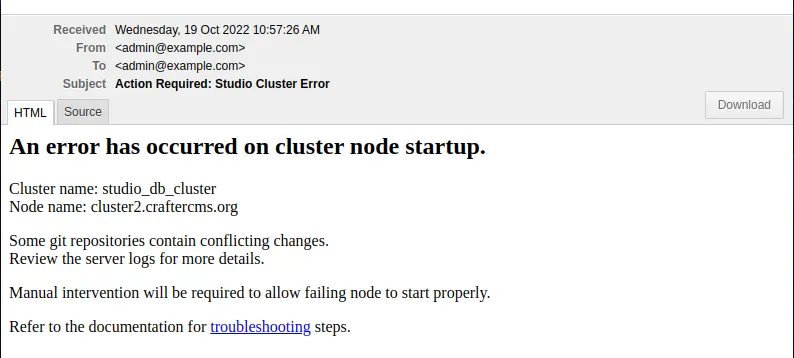
If there is any divergent history, the node will fail to startup and the admins would need to remove any commits “ahead” of primary branch. That would apply for all repositories (global, site sandbox, site published).
After reviewing the logs (tomcat logs and git log), there are a few ways to go about fixing the sync problem:
Manually remove the extra commits, do a
git reset --hardManually move the extra commits into the primary corresponding repository
Shutdown new primary and start the failing one as primary
Changing the Cluster Git URL
When the cluster Git URL for syncing members is changed after a cluster has been setup and started, the nodes on the disk may contain the old URL format when starting up. The following error appears in the log when switching the URL from SSH to HTTPS:
[ERROR] 2021-03-12T18:54:02,887 [pool-5-thread-10] [job.StudioClockExecutor] | Error executing Studio Clock Job java.lang.ClassCastException: org.eclipse.jgit.transport.TransportHttp cannot be cast to org.eclipse.jgit.transport.SshTransport
To sync the Git URL format on disk with the new format set in the config, the remotes will need to be recreated
To recreate a remote:
Stop the cluster
Update the configuration file with the desired URL format in all your nodes
bin/apache-tomcat/shared/classes/crafter/studio/extension/studio-config-override.yaml# Cluster Git URL format for synching members. # - Typical SSH URL format: ssh://{username}@{localAddress}{absolutePath} # - Typical HTTPS URL format: https://{localAddress}/repos/sites studio.clustering.sync.urlFormat: ssh://{username}@{localAddress}{absolutePath}
Remove the remotes in all your nodes via the command line interface using
gitin theglobalrepo and thesandboxandpublishedrepos of all the sites in the cluster.The global repo is located in CRAFTER_HOME/data/repos/global, the
sandboxrepo of a site is located in CRAFTER_HOME/data/repos/sites/<site-name>/sandbox and thepublishedrepo of a site is located in CRAFTER_HOME/data/repos/sites/<site-name>/publishedThe cluster remote names are available from
Clusterin the Studio global menu.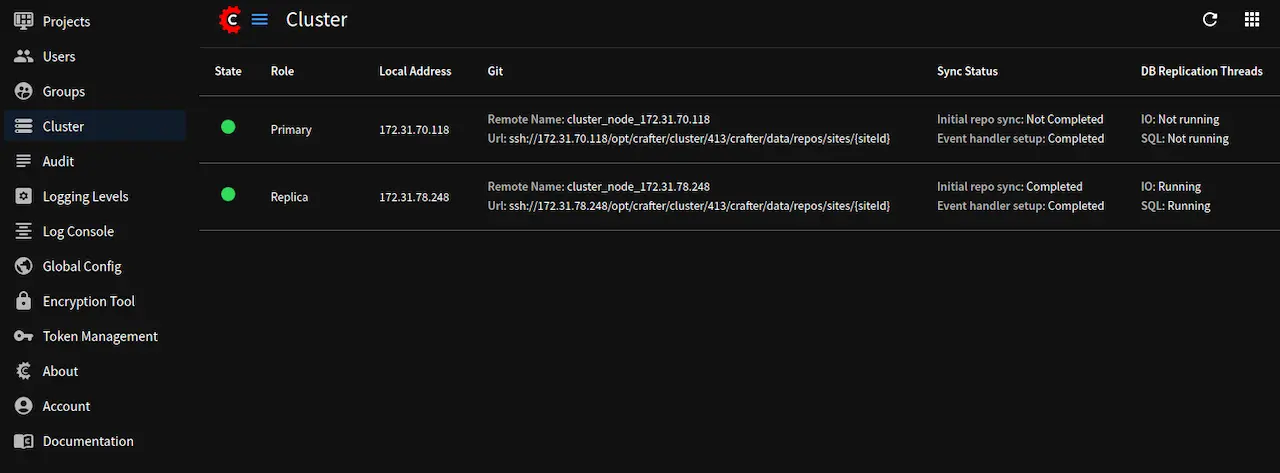
Remember to only remove the cluster remotes. Cluster remote names start with
cluster_. See example below:List of remotes for the sandbox repository of site video$ git remote -v cluster_node_192.168.1.103 ssh://myuser@192.168.1.103/opt/crafter/data/repos/sites/video/sandbox (fetch) cluster_node_192.168.1.103 ssh://myuser@192.168.1.103/opt/crafter/data/repos/sites/video/sandbox (push) origin https://github.com/craftercms/video-center-blueprint.git (fetch) origin https://github.com/craftercms/video-center-blueprint.git (push)
To remove a remote, run
git remote rm <remote_name>, whereremote_nameis the name of remote as seen from theClusterscreen in the Studio Main Menu. Let’s use the remote namecluster_node_192.168.1.103for our example on removing a remoteRemove remote$ git remote rm cluster_node_192.168.1.103
To verify the remotes are gone on disk, view the current remotes and make sure that the list does not contain a remote with a name beginning with
cluster_xxxx:View current remotes$ git remote -v origin https://github.com/craftercms/video-center-blueprint.git (fetch) origin https://github.com/craftercms/video-center-blueprint.git (push)
Start the cluster. Once the cluster is started, the remotes will be recreated. Verify that the URL format displayed in
Clusterin the Studio global menu is the desired URL format.