Build a Form Engine Data Source
What is a Data Source
Crafter Studio form controls should be written in a way that makes them independent of the data they allow the user to select so that they can be (re)used across a wide range of data sets. To accomplish this objective we use a data source pattern where by the form control widget code is concerned with rendering and facilitating the data capture/selection process but delegates the retrieval of the content to a separate swappable component interface known as a data source.
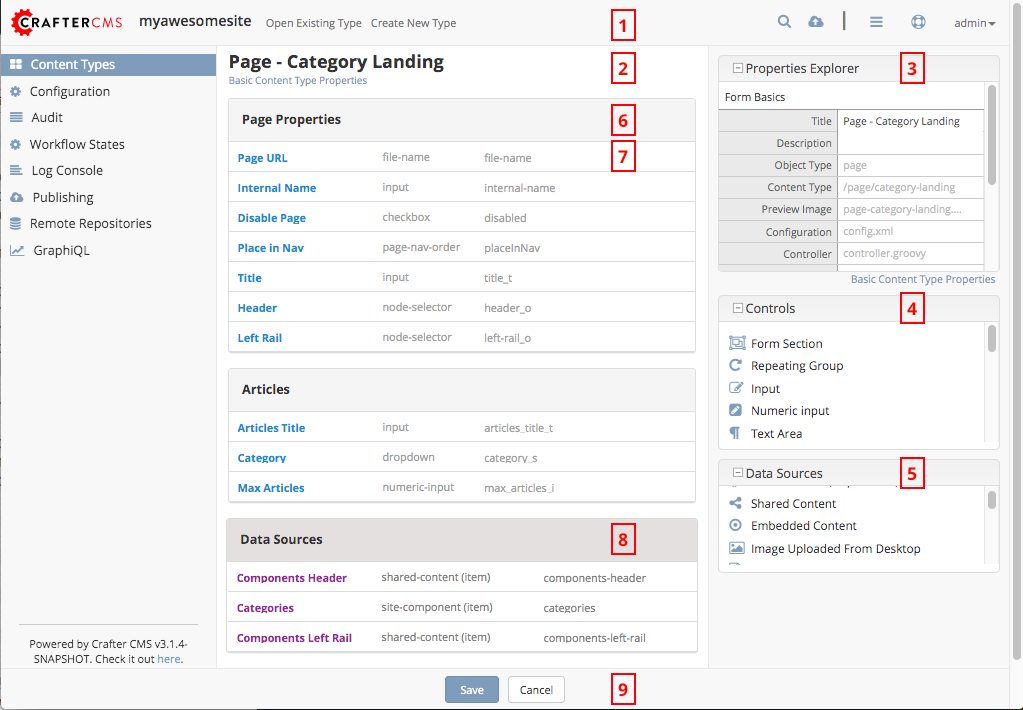
Form Engine data sources are #5 in the image above.
Out of the box data sources are:
The anatomy of a Data Source Plugin
Data Sources consist of (at a minimum)
A single javascript file which implements the data source interface.
The file name of the data source is important as the system uses a convention whereby the JS file name and the data source name in the configuration must be the same.
The module name must also be the same as the data source name with
cstudio-forms-controls-prepended to the front of it Ex:cstudio-forms-controls-configured-list
Configuration in a Crafter Studio project to make that data source available for use.
Data Source Interface
Data Source Interface
1 /**
2 * Constructor: Where .X is substituted with your class name
3 */
4 CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList = CStudioForms.Datasources.X ||
5 function(id, form, properties, constraints) {
6 }
7
8 /**
9 * Extension of the base class
10 */
11 YAHOO.extend(CStudioForms.Datasources.X, CStudioForms.CStudioFormDatasource, {
12
13 /**
14 * Return a user friendly name for the data source (will show up in content type builder UX
15 */
16 getLabel: function() { },
17
18 /**
19 * return a string that represents the type of data returned by the data source
20 * This is often of type "item"
21 */
22 getInterface: function() { },
23
24 /**
25 * return a string that represents the kind of data source (this is the same as the file name)
26 getName: function() { },
27
28 /**
29 * return a list of properties supported by the data source.
30 * properties is an array of objects with the following structure { label: "", name: "", type: "" }
31 */
32 getSupportedProperties: function() { },
33
34 /**
35 * method responsible for getting the actual values. Caller must pass callback which meets interface:
36 * { success: function(list) {}, failure: function(exception) }
37 */
38 getList: function(cb) { }
39 });
Coding an example
Our example is a data source that gets values from an XML file stored in the repository. This is a simple data source that allows administrators to define common taxonomies or lists and then to re-use those across many forms without having to redefine them every time.
Data Source Code
Location /STUDIO-WAR/default-site/static-assets/components/cstudio-forms/data-sources/configured-list.js
1 /**
2 * Constructor. This data source can take time to retrieve the content from the repository.
3 * For this reason when a caller asks for data we look to see if the data has already been returned.
4 * If not we register the request to call back later. Otherwise, we returned the cached data.
5 * The constructor initializes the data source and then immediately starts working on retrieving and caching the data.
6 * Once the data is returned waiting controls are called back.
7 */
8 CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList = CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList ||
9 function(id, form, properties, constraints) {
10 this.id = id;
11 this.form = form;
12 this.properties = properties;
13 this.constraints = constraints;
14 this.callbacks = [];
15 var _self = this;
16
17 for(var i=0; i<properties.length; i++) {
18 var property = properties[i]
19 if(property.name == "listName") {
20 var cb = {
21 success: function(config) {
22 var values = config.values;
23 if(!values.length) {
24 values = [ values.value ];
25 }
26
27 _self.list = values;
28
29 for(var j=0; j<_self.callbacks.length; j++) {
30 _self.callbacks[j].success(values);
31 }
32 },
33 failure: function() {
34 }
35 };
36
37 CStudioAuthoring.Service.lookupConfigurtion(
38 CStudioAuthoringContext.site,
39 "/form-control-config/configured-lists/" + property.value + ".xml",
40 cb);
41
42 }
43 }
44
45 return this;
46 }
47
48 /**
49 * extend the base class and override required methods
50 */
51 YAHOO.extend(CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList, CStudioForms.CStudioFormDatasource, {
52
53 getLabel: function() {
54 return "Configured List of Values";
55 },
56
57 getInterface: function() {
58 return "item";
59 },
60
61 getName: function() {
62 return "configured-list";
63 },
64
65 getSupportedProperties: function() {
66 return [
67 { label: "List Name", name: "listName", type: "string" }
68 ];
69 },
70
71
72 /**
73 * if the list is cached return it otherwise register the request for a callback when it is available
74 */
75 getList: function(cb) {
76 if(!this.list) {
77 this.callbacks[this.callbacks.length] = cb;
78 }
79 else {
80 cb.success(this.list);
81 }
82 },
83
84
85 });
86
87 CStudioAuthoring.Module.moduleLoaded("cstudio-forms-controls-configured-list", CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList);
Configuring the Data source to show up in Crafter Studio
Add the datasources name to the list of data sources in the content type editor
Location (In Repository) SITENAME/config/studio/administration/site-config-tools.xml
1 <config>
2 <tools>
3 <tool>
4 <name>content-types</name>
5 <label>Content Types</label>
6 <controls>
7 ...
8 </controls>
9 <datasources>
10 ...
11 <datasource>video-desktop-upload</datasource>
12 <datasource>configured-list</datasource>
13 </datasources>
14 ...
15 </tool>
16 <!--tool>...</tool -->
17 </tools>
18 </config>
Complex Example that uses AJAX to get data from external source:
1 CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList = CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList ||
2 function(id, form, properties, constraints) {
3 this.id = id;
4 this.form = form;
5 this.properties = properties;
6 this.constraints = constraints;
7 this.callbacks = [];
8 var _self = this;
9
10 for(var i=0; i<properties.length; i++) {
11 var property = properties[i]
12 if(property.name == "listName") {
13 var cb = {
14 success: function(config) {
15 var values = config.values;
16 if(!values.length) {
17 values = [ values.value ];
18 }
19
20 _self.list = values;
21
22 for(var j=0; j<_self.callbacks.length; j++) {
23 _self.callbacks[j].success(values);
24 }
25 },
26 failure: function() {
27 }
28 };
29
30 CStudioAuthoring.Service.lookupConfigurtion(
31 CStudioAuthoringContext.site,
32 "/form-control-config/configured-lists/" + property.value + ".xml",
33 cb);
34
35 }
36 }
37
38 return this;
39 }
40 YAHOO.extend(CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList, CStudioForms.CStudioFormDatasource, {
41 getLabel: function() {
42 return "Configured List of Values";
43 },
44 getInterface: function() {
45 return "item";
46 },
47 /*
48 * Datasource controllers don't have direct access to the properties controls, only to their properties and their values.
49 * Because the property control (dropdown) and the dataType property share the property value, the dataType value must stay
50 * as an array of objects where each object corresponds to each one of the options of the control. In order to know exactly
51 * which of the options in the control is currently selected, we loop through all of the objects in the dataType value
52 * and check their selected value.
53 */
54 getDataType : function getDataType () {
55 var val = null;
56 this.properties.forEach( function(prop) {
57 if (prop.name == "dataType") {
58 // return the value of the option currently selected
59 prop.value.forEach( function(opt) {
60 if (opt.selected) {
61 val = opt.value;
62 }
63 });
64 }
65 });
66 return val;
67 },
68 getName: function() {
69 return "configured-list";
70 },
71
72 getSupportedProperties: function() {
73 return [{
74 label: "Data Type",
75 name: "dataType",
76 type: "dropdown",
77 defaultValue: [{ // Update this array if the dropdown options need to be updated
78 value: "value",
79 label: "",
80 selected: true
81 }, {
82 value: "value_s",
83 label: "String",
84 selected: false
85 }, {
86 value: "value_i",
87 label: "Integer",
88 selected: false
89 }, {
90 value: "value_f",
91 label: "Float",
92 selected: false
93 }, {
94 value: "value_dt",
95 label: "Date",
96 selected: false
97 }, {
98 value: "value_html",
99 label: "HTML",
100 selected: false
101 }]
102 }, {
103 label: "List Name",
104 name: "listName",
105 type: "string"
106 }];
107 },
108 getSupportedConstraints: function() {
109 return [
110 { label: "Required", name: "required", type: "boolean" }
111 ];
112 },
113
114 getList: function(cb) {
115 if(!this.list) {
116 this.callbacks[this.callbacks.length] = cb;
117 }
118 else {
119 cb.success(this.list);
120 }
121 },
122
123 });
124 CStudioAuthoring.Module.moduleLoaded("cstudio-forms-controls-configured-list", CStudioForms.Datasources.ConfiguredList);
Summary
A good place to start is by looking at the control you want to use, for example the video picker.
Location /STUDIO-WAR/default-site/static-assets/components/cstudio-forms/controls/video-picker.js
When you want to build a data source, there is a method called get interface. This method tells the system what the data source can help with. So using the same example, a video upload returns video and thus the video picker can use that data source.
Location /STUDIO-WAR/default-site/static-assets/components/cstudio-forms/data-sources/video-desktop-upload.js
If you want to create a new datasource for the video picker, you basically copy and paste a similar datasource, then change the object class name, label and interface. Then in the project go to the the administration panel and change the configuration to load the new javascript file.





























