Working with GraphQL
Warning
GraphQL requires Elasticsearch. If your site is using Crafter Search/Solr as the search engine, GraphQL will not work.
To update your sites to Elasticsearch, follow the guide Migrating a site from Solr to Elasticsearch
CrafterCMS provides built-in support for GraphQL to query content in any site without writing additional code. A GraphQL schema is generated independently for each site based on the content-type configuration that has been created using Crafter Studio, and the schema is automatically updated after any change is detected.
To implement a site that uses GraphQL you would follow a workflow like this:
Create a new site (if needed, for existing sites skip to step number 3)
Define the content model for your site
Obtain the GraphQL schema for your site, you can use the provided GraphiQL client or any third party client
Develop GraphQL queries to use in your site or external app
All content changes made by authors in Crafter Studio will be immediately available in GraphQL queries.
When a change is made in the content model, for example adding a new field or creating a new content-type, the GraphQL schema will be rebuilt to reflect the same changes. So for a CrafterCMS site that uses GraphQL queries the development process would look like this:
Developers define the base content model
Developers define the site base GraphQL queries to use the latest schema
Content authors create content based on the model
Publishers review & approve the author’s work
Publishers publish to live both the content model configuration & the content updates
Crafter Deployer will handle the GraphQL schema rebuild in delivery
You can also use the CrafterCMS GraphQL API from an external site or application, however in this case you will need to handle the schema reload using third party tools.
Using GraphiQL in Crafter Studio
GraphiQL is a simple GraphQL client that you can use in Crafter Studio to run GraphQL queries and explore the schema documentation for a site without the need of any other tool. To access GraphiQL follow these steps:
Login to Crafter Studio
Click
Dashboardnext to the name of your siteClick
Site Configin the left sidebarClick
GraphiQLin the left sidebar
To explore the GraphQL schema you can click the Docs icon on the right side:

GraphiQL provides a convenient search navigation to quickly find a specific type or field:
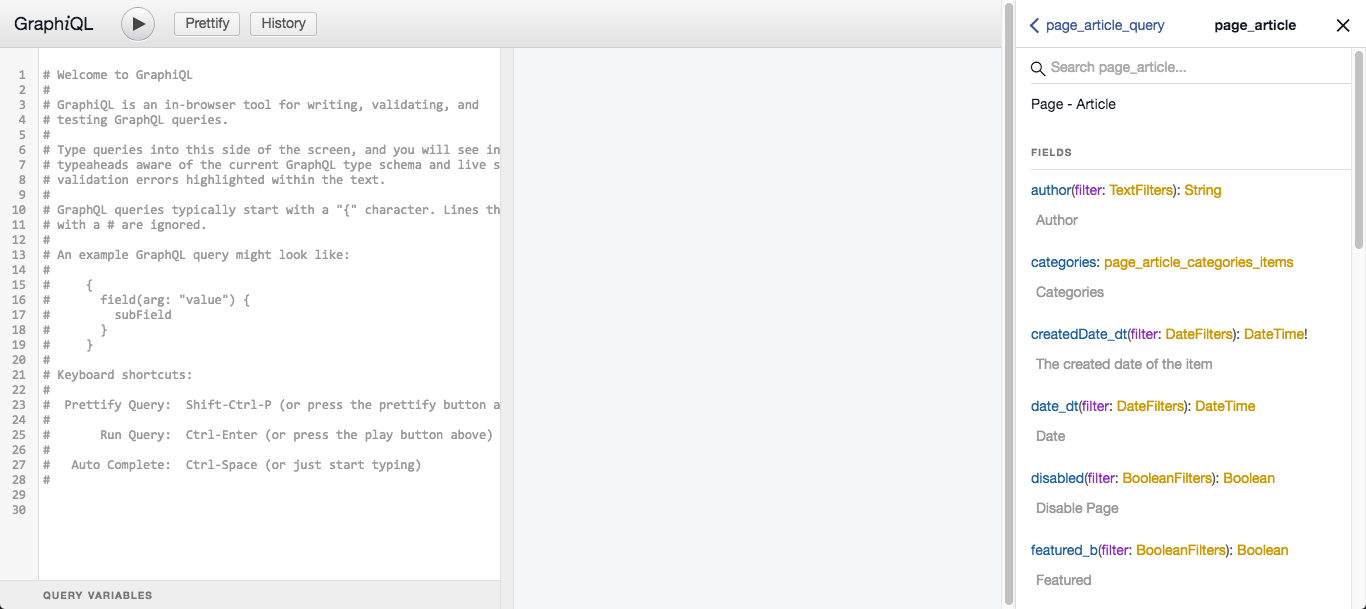
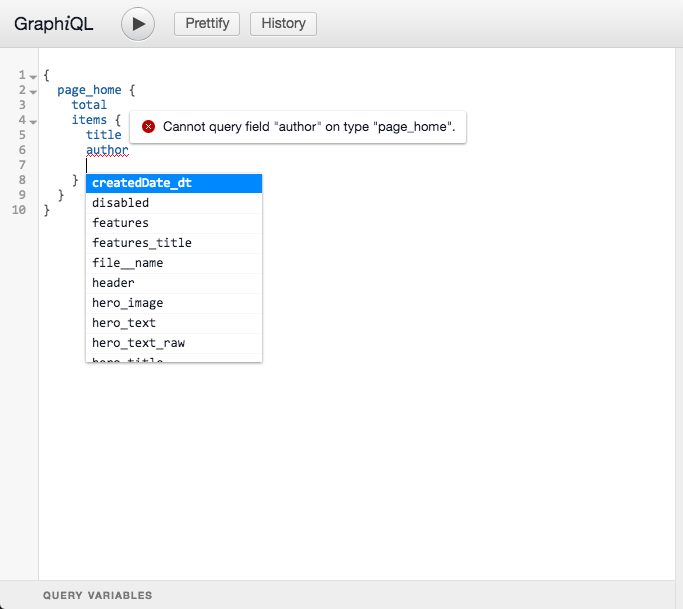
To test GraphQL queries type them in the left text editor, GraphiQL will provide suggestions and validate the query against the schema in real time.
Note
If the GraphQL server host name used is not localhost, the <graphql-server-url /> in your proxy configuration file needs to be set to the appropriate url. For more information on the proxy configuration file, see: Proxy Configuration
GraphQL Examples
Here you can find some examples on how to query content using GraphQL. The following examples use the built-in
Website Editorial blueprint but the same concepts apply to any CrafterCMS site.
For each content-type in the site you will find a field in the root Query, the name of the field is based on the
name of the content-type so for /page/article the field will be page_article.
These fields contain two sub-fields, one is the total number of items found by the query and the other is a list
of items.
Note
Because GraphQL only supports the underscore _ character besides alphanumeric for names, if your content-type or
field name contains the dash - character it will be replaced with a double underscore __. To avoid
unnecessary long names it is suggested to use only _ or camelCase notation if possible.
One of simplest GraphQL queries you can run in CrafterCMS sites is to find all items of a given content-type.
/page/article items 1# root query
2{
3 # query for content-type '/page/article'
4 page_article {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # content-type fields that will be returned
8 # (names are based on the content-type configuration)
9 title
10 author
11 date_dt
12 }
13 }
14}
You can also run queries to find all pages, components or content items (both pages and components).
1# root query
2{
3 # query for all pages
4 pages {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # the page fields that will be returned
8 content__type
9 localId
10 createdDate_dt
11 lastModifiedDate_dt
12 placeInNav
13 orderDefault_f
14 navLabel
15 }
16 }
17}
1# root query
2{
3 # query for all pages
4 components {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # the component fields that will be returned
8 content__type
9 localId
10 createdDate_dt
11 lastModifiedDate_dt
12 }
13 }
14}
1# root query
2{
3 # query for all pages
4 contentItems {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # the content item fields that will be returned
8 content__type
9 localId
10 createdDate_dt
11 lastModifiedDate_dt
12 }
13 }
14}
As you can expect if there are too many items for a given query the result will be too large, so you can also
implement pagination using the offset and limit parameters. For example the following query
will return only the first five items found.
/page/article 1# root query
2{
3 # query for content-type '/page/article'
4 page_article(offset: 0, limit: 5) {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # content-type fields that will be returned
8 # (names are based on the content-type configuration)
9 title
10 author
11 date_dt
12 }
13 }
14}
By default all items will be sorted using the lastModifiedDate_dt in descending order, you can change it by using
the sortBy and sortOrder parameters. For example you can use the date_dt field that is specific for the
/page/article content-type to sort.
/page/article 1# root query
2{
3 # query for content-type '/page/article'
4 page_article (offset: 0, limit: 5, sortBy: "date_dt", sortOrder: ASC) {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # content-type fields that will be returned
8 # (names are based on the content-type configuration)
9 title
10 author
11 date_dt
12 }
13 }
14}
Besides finding all items for a specific content-type, it is also possible to filter the results using one or more fields in the query. Fields will have different filters depending on their type, for example you can find items for a specific author.
/page/article 1# root query
2{
3 # query for content-type '/page/article'
4 page_article (offset: 0, limit: 5, sortBy: "date_dt", sortOrder: ASC) {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # content-type fields that will be returned
8 # (names are based on the content-type configuration)
9 title
10 # only return articles from this author
11 author (filter: { equals: "Jane Doe" })
12 date_dt
13 }
14 }
15}
Additionally you can create complex filters using expressions like and, or and not for any field:
1# Root query
2{
3 page_article {
4 total
5 items {
6 title
7 author
8 date_dt
9 # Filter articles that are not featured
10 featured_b (
11 filter: {
12 not: [
13 {
14 equals: true
15 }
16 ]
17 }
18 )
19 # Filter articles from category style or health
20 categories_o {
21 item {
22 key (
23 filter: {
24 or: [
25 {
26 matches: "style"
27 },
28 {
29 matches: "health"
30 }
31 ]
32 }
33 )
34 value_smv
35 }
36 }
37 }
38 }
39}
You can also include fields from child components in your model, this applies to fields like node-selector,
checkbox-group and repeat groups. Filters can also be added to fields from child components.
/page/article using child components 1# root query
2{
3 # query for content-type '/page/article'
4 page_article (offset: 0, limit: 5, sortBy: "date_dt", sortOrder: ASC) {
5 total # total number of items found
6 items { # list of items found
7 # content-type fields that will be returned
8 # (names are based on the content-type configuration)
9 title
10 # only return articles from this author
11 author (filter: { equals: "Jane Doe" })
12 date_dt
13 categories_o {
14 item {
15 # only return articles from this category
16 key (filter: { matches: "health" })
17 value_smv
18 }
19 }
20 }
21 }
22}
GraphQL aliases are supported on root level query fields (contentItems, pages, components and content
type fields).
1# root query
2{
3 # query for 2016 articles
4 articlesOf2016: page_article {
5 items {
6 localId(filter: {regex: ".*2016.*"})
7 }
8 },
9 # query for 2017 articles
10 articlesOf2017: page_article {
11 items {
12 localId(filter: {regex: ".*2017.*"})
13 }
14 }
15}
GraphQL fragments are fully supported and can be used inline or as spreads. Using fragments you can simplify
queries by extracting repeated fields or request specific fields for different content-types in as single query:
1# Fragment definition
2fragment CommonFields on ContentItem {
3 localId
4 createdDate_dt
5}
6
7# Root query
8query {
9 page_article {
10 total
11 items {
12 # Fragment spread
13 ... CommonFields
14 title
15 author
16 }
17 }
18
19 component_feature {
20 total
21 items {
22 # Fragment spread
23 ... CommonFields
24 title
25 icon
26 }
27 }
28}
1# Root query
2{
3 contentItems {
4 total
5 items {
6 # Query for fields from the interface
7 localId
8 createdDate_dt
9
10 # Query for fields from specific types
11 ... on page_article {
12 title
13 author
14 }
15
16 ... on component_feature {
17 title
18 icon
19 }
20 }
21 }
22}
For more detailed information about GraphQL you can read the official documentation.