Content Modeling
Every content object in CrafterCMS is an object associated with a Content Model. Content Models allow you to add structure to your content and facilitate consumption via various visual representations or via APIs. One of the great things about CrafterCMS content models is that your content can be semi-structured which allows content authors the freedom to be as creative as they’d like to be, but provide the template/UI and API developers enough structure to produce solid multi-channel renditions of the content. This section will walk you through Content Type management in Crafter Studio to help you create the models that best fit your requirements.
Content Types in Crafter Studio
Content Type Management in Crafter Studio is located in the ![]() .
.
Content Types are limited to two core types: Pages and Components. Both are made up of three ingredients:
Model: The content pieces that will be captured from the content authors for the page or component
View: The view template that will render the content, typically to HTML markup
Controller: The controller that handles the incoming request for the page or component
Pages
Pages are top-level container types. Pages hold content, and optionally components. Content within pages is made up of various types, for example content can be a date, an image, or a rich text field.
Components
Components only differ from pages in that they can’t render by themselves, instead, they must render within a container page or another component.
Content Type Model Definition
Content models are defined via Crafter Studio’s graphical modeling tool under Content Types:
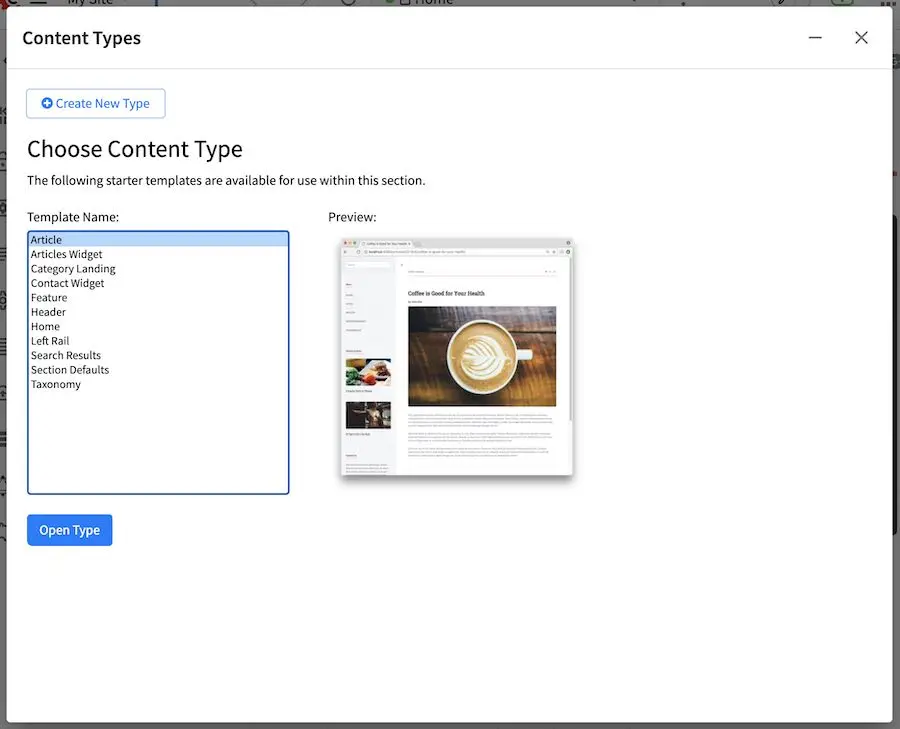
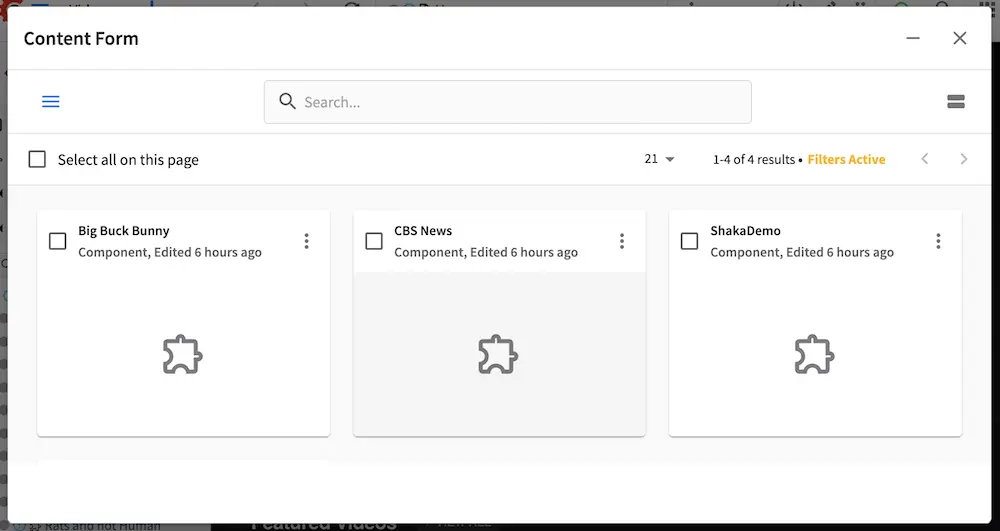
You can now either create a new content type or open an existing type. Creating a new content type brings up a dialog that requests some basic content type information.
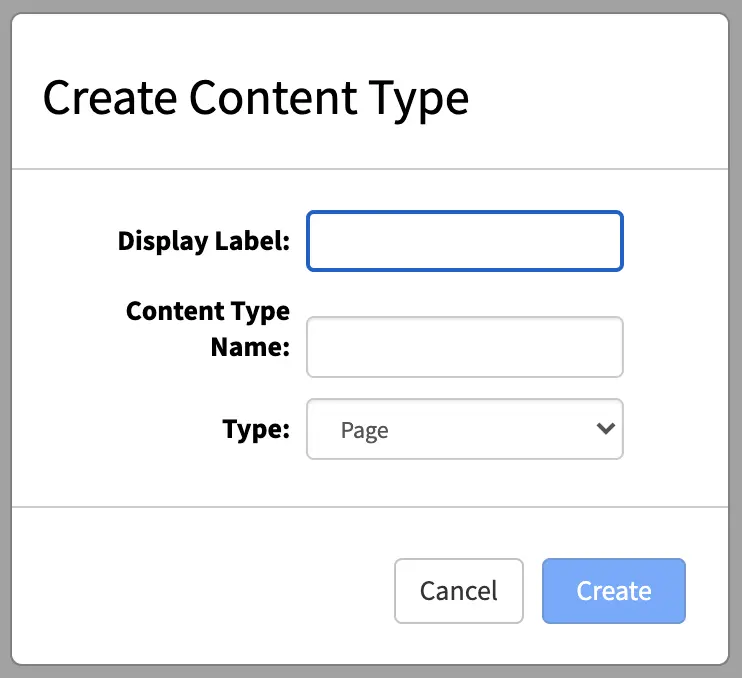
You now specify:
Display Label: The name of your new content type as you’ll see it in Crafter Studio.
Content Type Name: The low-level system name of your content type, this field will be automatically generated for you. Modify this only if you know what you’re doing.
Type: Choose if you’re defining a Page or a Component.
Note
Content Type Name will be removed in a future release in favor of full automation of name generation with collision resolution mechanics.
Form Builder Basics
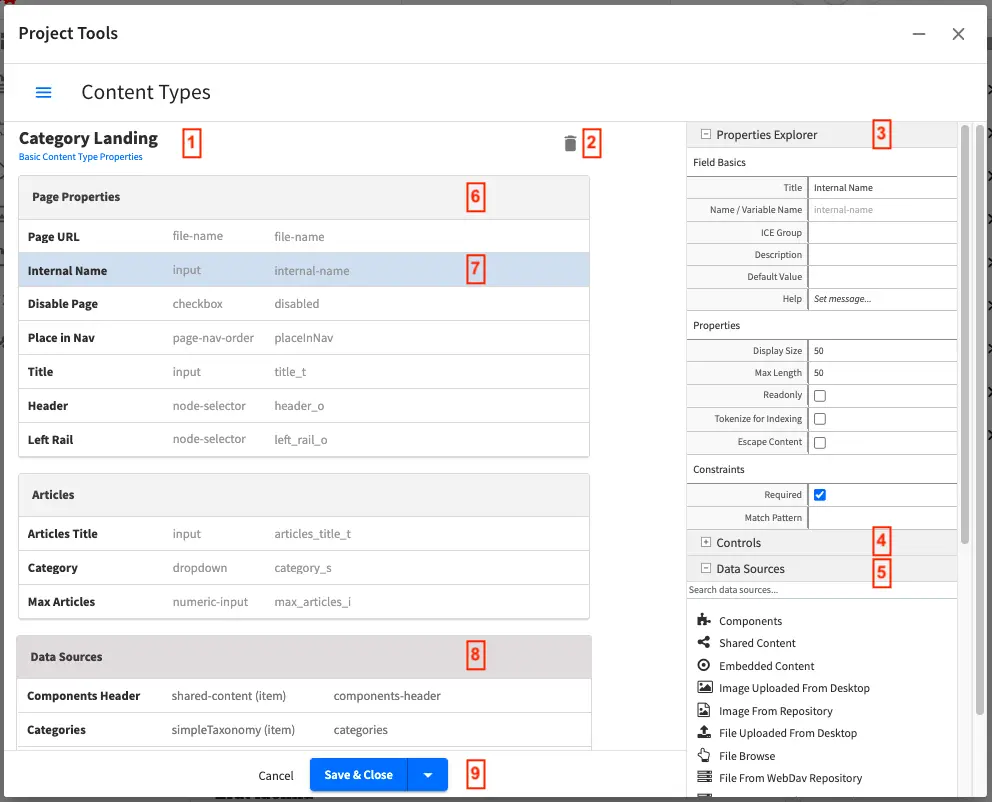
Crafter Studio’s Form Builder
Label
|
Description
|
1
|
Form Builder: The beginning of the form builder and it’s headed by the name of the
currently open Content Type.
Click here to explore the global properties of the type in the Properties Explorer,
#3.
|
2
|
Delete Icon: Deletes the current content type
|
3
|
Properties Explorer: Helps configure the properties of the currently
selected item. Clicking on an item on the left side of the screen,
like #2 or #7 will populate this control and allow you to modify
the selected item.
|
4
|
Form Controls: This is a list of available form controls for you to build your own
form with. Note that the list can be expanded or collapsed and a search can also be
performed instead of scrolling through the list.
Controls can be dragged from the controls list onto the form builder.
|
5
|
Data Sources: Shows the list of available data sources that can be attached to this
content type such that the content authors can pull content and incorporate it into
pages or components. Data Sources can be dragged over to the form builder
and configured as needed.
The content author will then use the control to pull data from that data source into
the content object.
|
6
|
Form Section: Form sections help cluster a number of controls together to make it
easier for content authors. Click on the form section to edit its properties in
the Properties Explorer.
|
7
|
Form Canvas: Actual controls that have been placed on this form.
Clicking on a control will allow you to configure this control in the Properties
Explorer.
|
8
|
Data Source: The data sources configured for this content type.
To configure a data source, click on it and then edit the properties
in the Properties Explorer.
|
9
|
Save, Save & Close, Save & Minimize or Cancel the changes to the Content Type.
|
Properties of Content Types
Let’s select the content type itself, by clicking on the content type name at the top of the Form Builder and explore its properties.
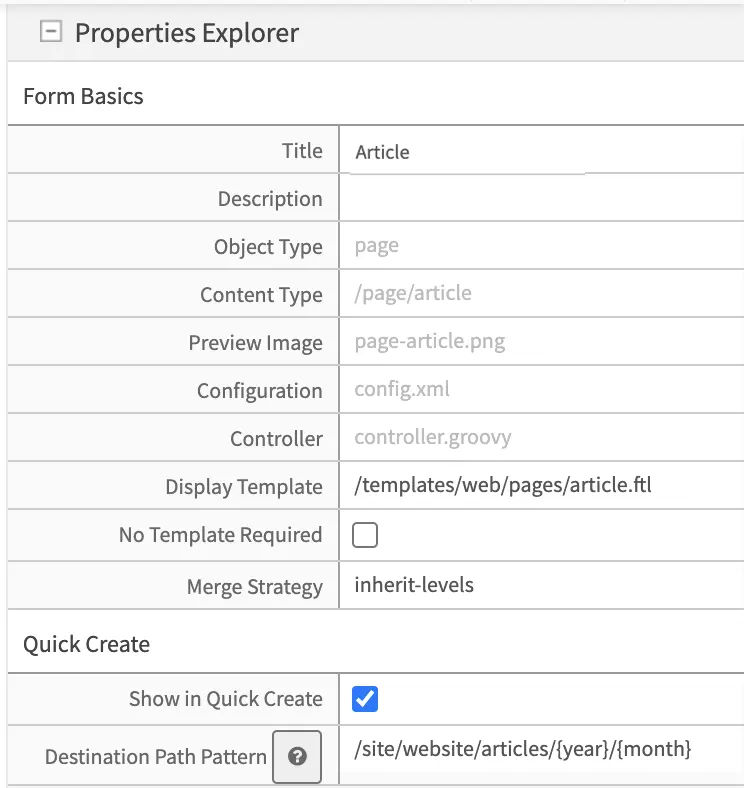
The fields available at this level are:
Field
|
Description
|
Title
|
Content Type’s friendly name
|
Description
|
Description of the Content Type
|
Object Type
|
Page or Component (read only)
|
Content Type
|
System name and path of this content type (read only)
|
Preview
Image
|
An image that reflects what an instance of this content item might look like.
It will be shown in the user interface when creating new content instances.
|
Configuration
|
Contains config.xml which holds information about the content type such as the
limit where content can be created, is it previewable, etc.
|
Controller
|
Contains controller.groovy which provides an extension/hook to authoring
lifecycle events.
|
Display
Template
|
View template to use when rendering this content
|
Merge
Strategy
|
The inheritance pattern to use with content of this type, please see Content
Inheritance for more detail on this feature Content Inheritance
|
Show in Quick
Create
|
Show this content type in the quick create menu from the context nav
|
Destination
Path Pattern
|
Path pattern where the content created from quick create will be stored.
The patterns available are the following:
{objectId} Inserts a GUID.
{year} Inserts the current year (4 digit year).
{month} Inserts the current month (2-digit month of the year).
{yyyy} Inserts the current year (4 digit year).
{mm} Inserts the current month (2-digit month of the year).
{dd} Inserts the current day (2-digit day of the month).
|
The 2 key properties are: the display template (Content Type View Templates) which is the HTML template that renders the final Web page; the content inheritance (Content Inheritance) which determines how this content type will inherit from parent XML files in the system.
Content Creation Permissions
Limiting where a content type can be created is through the Configuration Property of a content type (config.xml) using the following tags:
1<paths>
2 <includes>
3 <pattern>REG_EXP_HERE</pattern>
4 </includes>
5</paths>
OR
1<paths>
2 <excludes>
3 <pattern>REG_EXP_HERE</pattern>
4 </excludes>
5</paths>
You can only use one of either include or exclude. Use Include when you need to whitelist places, use exclude when you need to blacklist.
We’ll look at an example of limiting where you can create content from the Website_Editorial blueprint that comes out of the box.
From the Sidebar, click on ![]() at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types then either create a new content type or open an existing content type. In the image below, we have the content type Article open for editing. Go to the Properties Explorer and click on Configuration. A pencil will appear next to the file name config.xml, click on that pencil to edit.
at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types then either create a new content type or open an existing content type. In the image below, we have the content type Article open for editing. Go to the Properties Explorer and click on Configuration. A pencil will appear next to the file name config.xml, click on that pencil to edit.
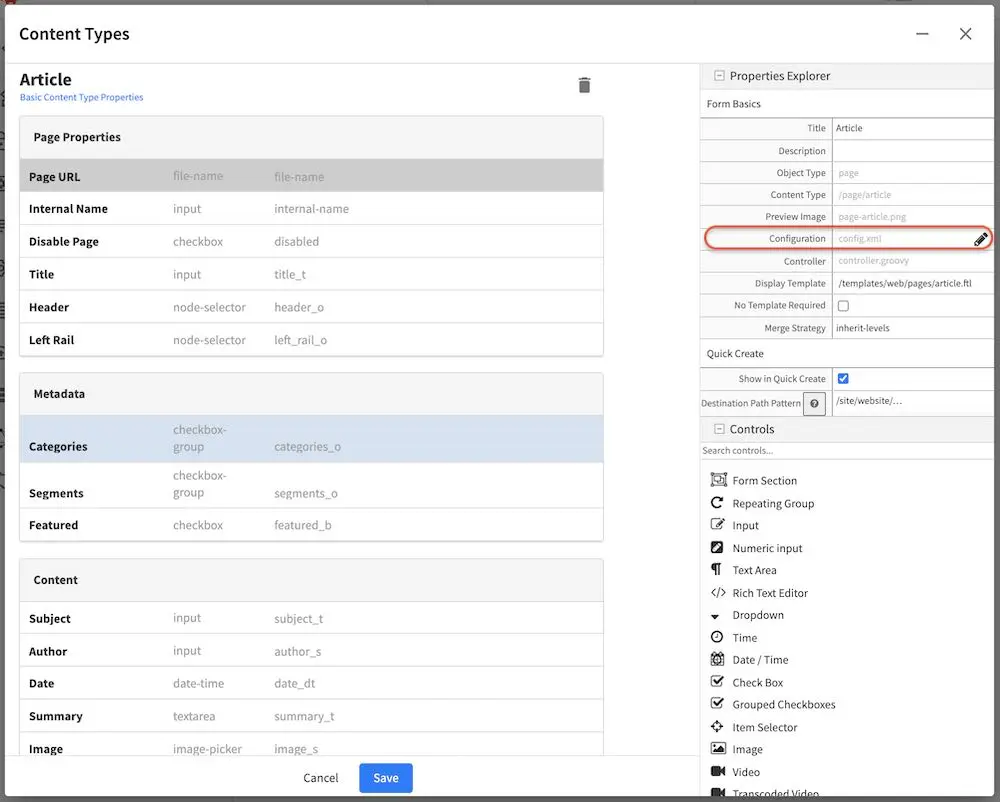
To limit where this particular content type can be created, the tags, <paths><includes><pattern>some_regex_pattern</pattern></includes></paths> are included towards the bottom of the file. Here, we can see that content type Article can be created anywhere under /site/website/articles
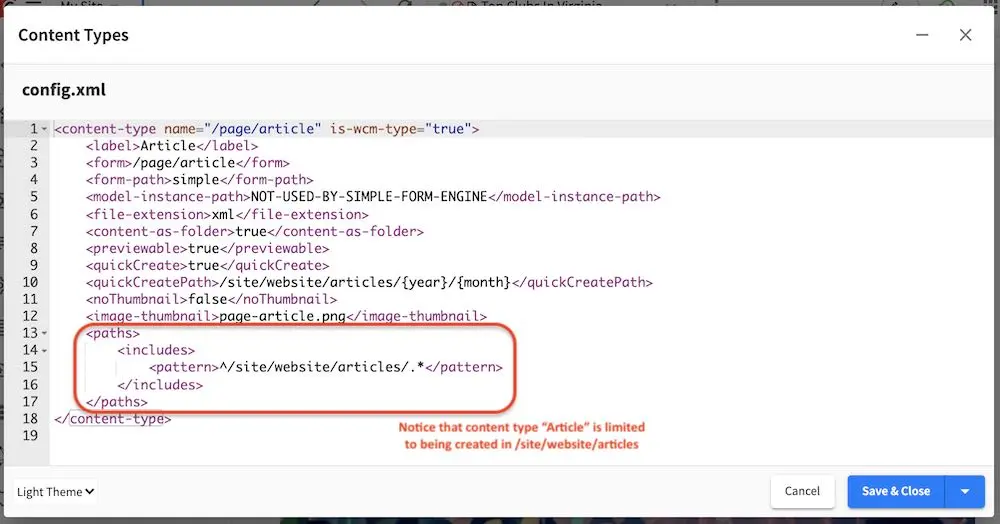
1<paths>
2 <includes>
3 <pattern>^/site/website/articles/.*</pattern>
4 </includes>
5</paths>
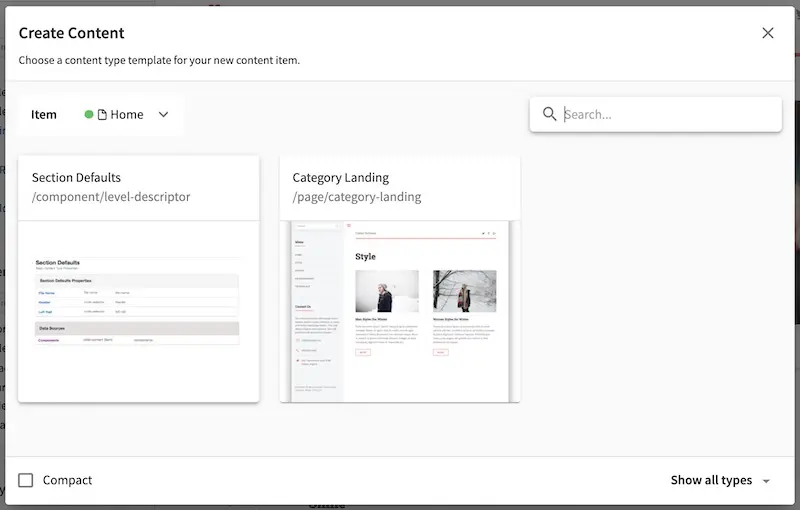
To see how the above tags/example works, go to the Sidebar and right click on the Home folder and select New Content. Notice that content type Article is not available from the content types listed.
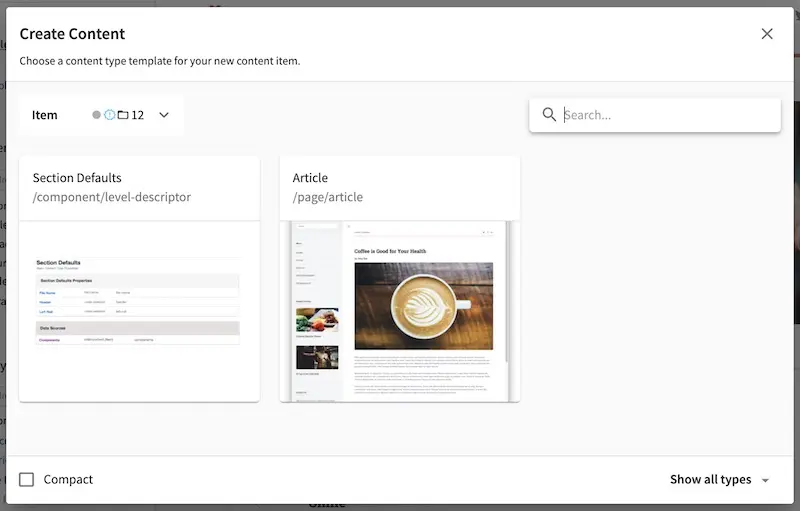
From the Sidebar again, navigate from the Pages folder to the /Home/articles/2020/12/ folder then right click and select New Content, notice that the content type Article is available from the list.
To see more examples, try creating content types in the other folders in the Sidebar such as the Taxonomy folder, the Components folder and anywhere under the Pages folder.
Cascade on Delete Configuration
Cascade on delete allows the automatic deletion of child items matching a regexp when a content is deleted.
Enabling cascade on delete is configured through the content type Configuration property (config.xml) using the following tags:
1<delete-dependencies>
2 <delete-dependency>
3 <pattern>REG_EXP_HERE</pattern>
4 <remove-empty-folder>false</remove-empty-folder>
5 </delete-dependency>
6</delete-dependencies>
We’ll look at an example of how to enable cascade on delete on the Article content type in the Website_editorial blueprint.
From the Sidebar, click on ![]() at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing. Next, go to the Properties Explorer and click on Configuration. A pencil will appear next to the file name config.xml, click on that pencil to edit.
at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing. Next, go to the Properties Explorer and click on Configuration. A pencil will appear next to the file name config.xml, click on that pencil to edit.
We’re going to enable cascade on delete for articles (Article content type) containing images under /static-assets/item/images, and we’ll also delete empty folders under /static-assets/item/images by adding the following code in the config.xml file:
1<delete-dependencies>
2 <delete-dependency>
3 <pattern>(^/static-assets/item/images/.*)</pattern>
4 <remove-empty-folder>true</remove-empty-folder>
5 </delete-dependency>
6</delete-dependencies>
To see cascade on delete in action, let’s create a new article (Article content type) under one of the article folders in the Sidebar. Enter data in the required fields and remember to upload from desktop an image in the Image field in the Content section. Click on the Save & Close button.
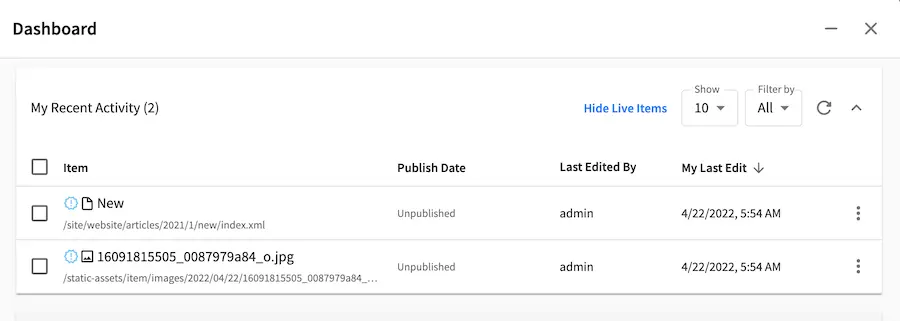
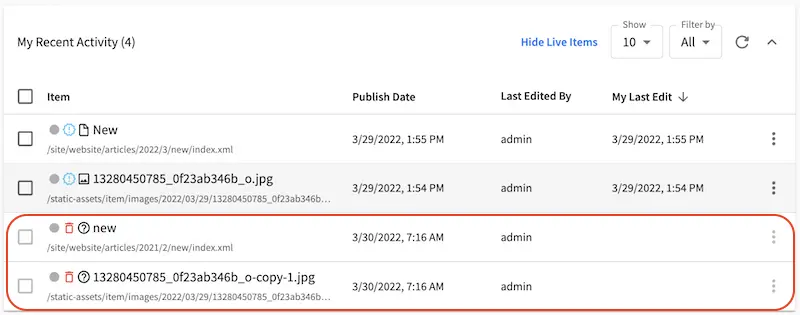
Let’s look at the dependencies of our newly created article, where we expect the image under the static-assets/items/images/2022/04/22 will be deleted when we delete the article since we have configured cascade on delete for content type Article for items under the directory static-assets/item/images:
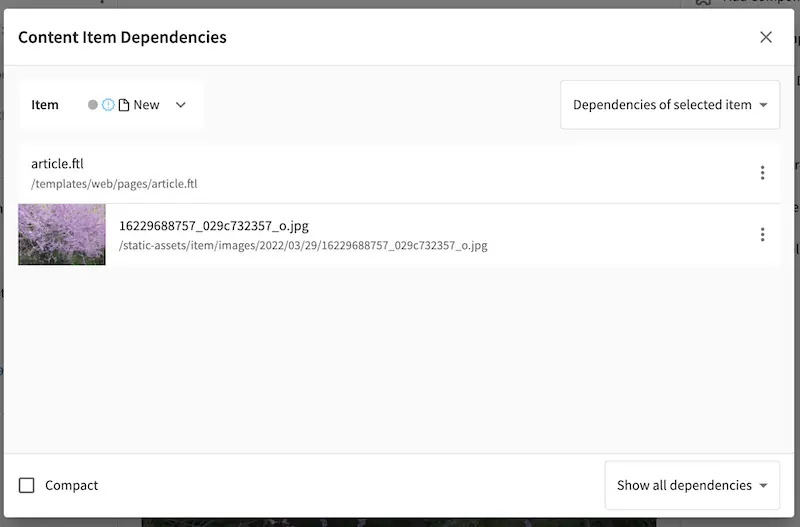
Open the Sidebar and navigate to the newly created article. Right click on the newly created article and select Delete. Open the Dashboard and notice the items listed as deleted in the My Recent Activity widget.
Note that there are default/configured protected folders that can’t be deleted. See here for more information.
Copy Dependencies Configuration
Copy dependencies allows the automatic copying of child items matching a regexp when a content is copied.
Enabling copy dependencies is configured through the content type Configuration property (config.xml) using the following tags:
1<copy-dependencies>
2 <copy-dependency>
3 <pattern>REG_EXP_HERE</pattern>
4 <target>FOLDER_FOR_COPIES</target>
5 </copy-dependency>
6</copy-dependencies>
We’ll look at an example of how to enable copy dependencies on the Article content type in the website editorial blueprint.
From the Sidebar, click on ![]() at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing. Next, go to the Properties Explorer and click on Configuration. A pencil will appear next to the file name config.xml, click on that pencil to edit.
at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing. Next, go to the Properties Explorer and click on Configuration. A pencil will appear next to the file name config.xml, click on that pencil to edit.
We’re going to enable copy dependencies for articles (Article content type) containing images under /static-assets/images/ and placing the copies in folder /static-assets/images/articles/ by adding the following code in the config.xml file:
1<copy-dependencies>
2 <copy-dependency>
3 <pattern>(^/static-assets/images/.*)</pattern>
4 <target>/static-assets/images/articles/</target>
5 </copy-dependency>
6</copy-dependencies>
Click on Save & Close, then save changes made to the content type by clicking on Save.
To see copy dependencies in action, let’s copy an article under one of the article folders from the Sidebar. First, we’ll create the folder articles under /static-assets/images. Next, we’ll navigate to articles/2020/12/Top Books For Young Women. Right click on the article and select Copy. Navigate to articles/2020/7, right click on the folder and select Paste.
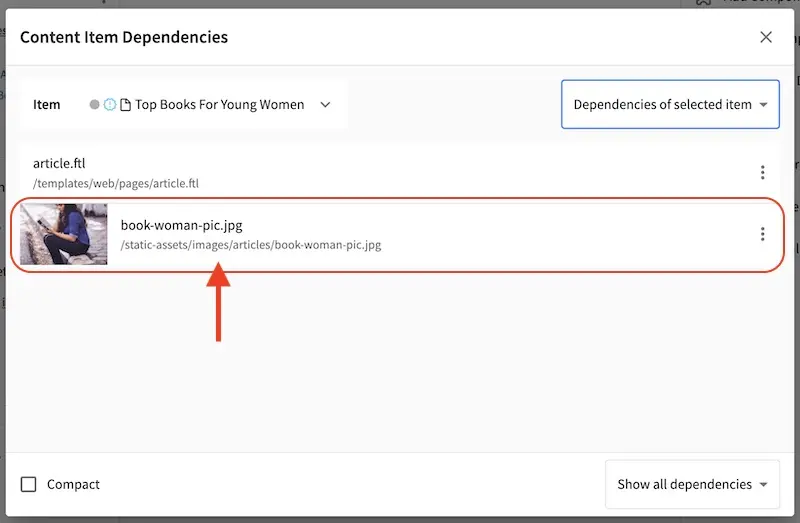
Let’s look at the dependencies of our copied article, where we expect a copy of the image under the static-assets/images/articles will be located since we have configured cop dependencies for content type Article for items under the directory static-assets/images:
Item Specific Dependencies
Item specific dependencies allows for the automatic copying of child items matching the regex pattern in the studio-config.yaml file when a content is copied. It also allows the automatic deletion of child items matching the regex pattern in the studio-config.yaml file when a content is deleted.
Below is the regex pattern for item specific dependencies:
# Regex pattern for item specific dependencies
studio.configuration.dependency.itemSpecificPatterns: /site/components/page/.*,/static-assets/page/.*,/site/components/item/.*,/static-assets/item/.*
/site/components/page/.* and /static-assets/page/.* are legacy regex pattern for backwards compatibility. Moving forward, we suggest using the following regex patterns for item specific dependencies: /site/components/item/.* and /static-assets/item/.*
Item specific dependencies are configured during content type creation. We’ll look at an example of how content is modeled to take advantage of item specific dependencies, using the Article content type in the website editorial blueprint.
From the Sidebar, click on ![]() at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing.
at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing.
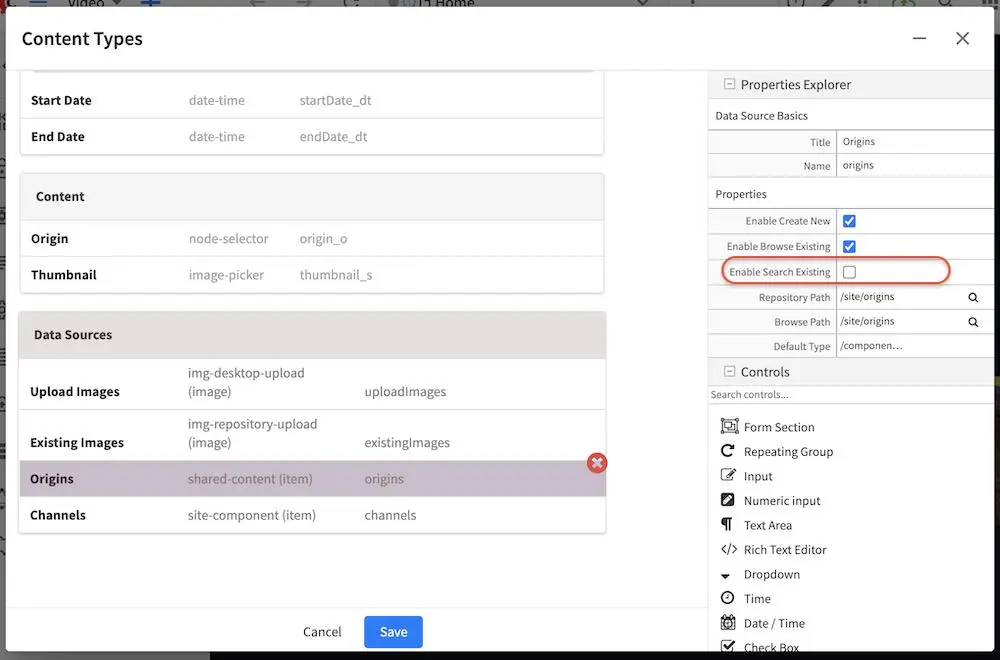
Scroll to the Data Sources section, and click on Upload Images. Notice the value in the Repository Path property, which is the path where to store the new file uploaded from desktop.
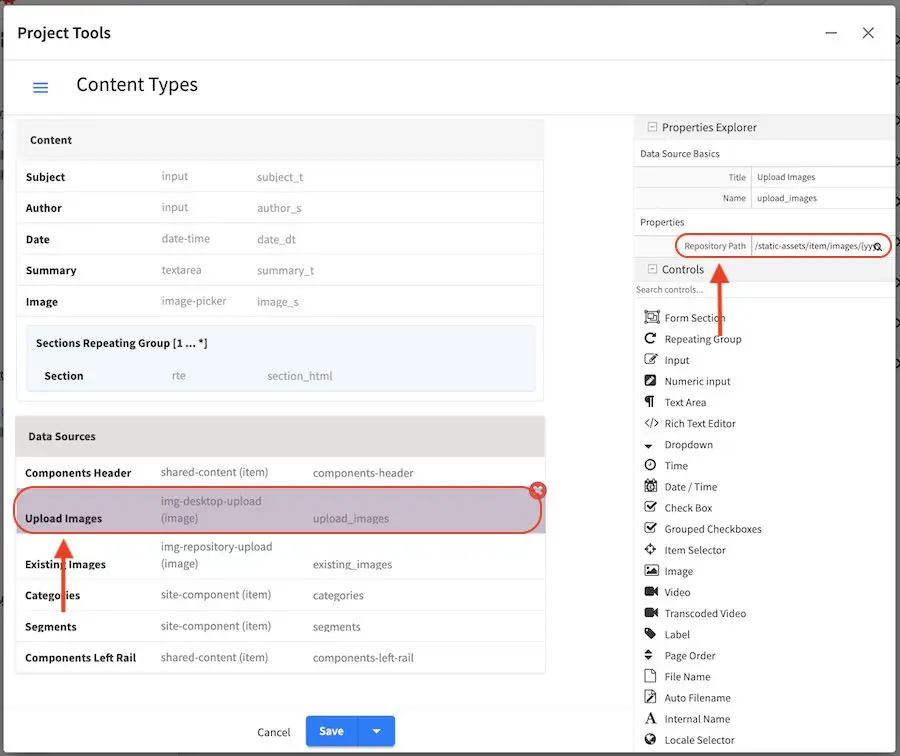
Let’s take a closer look at the value for the Repository Path property. The value listed is:
/static-assets/item/images/{yyyy}/{mm}/{dd}/
where:
{yyyy} inserts the current year when the image is uploaded (4 digit year)
{mm} inserts the current month when the image is uploaded (2-digit month of the year)
{dd} inserts the current day when the image is uploaded (2-digit day of the month)
To take advantage of item specific dependencies for copying and deleting, we will place uploaded items in /static-assets/item/. We added a folder image to better organize our items, since in this location, we will only be storing images. We also used the macros {yyyy}, {mm} and {dd}, again to better organize our image (we can browse by year, or by month, or by date). So, when an image is uploaded from the Desktop say on May 17, 2020, the image will be stored in the following location:
/static-assets/item/images/2020/05/17/
The macros {yyyy}, {mm} and {dd} are available for content modelers to use to better organize their project items. To see other macros available for content modelers, see Macros for Data Sources.
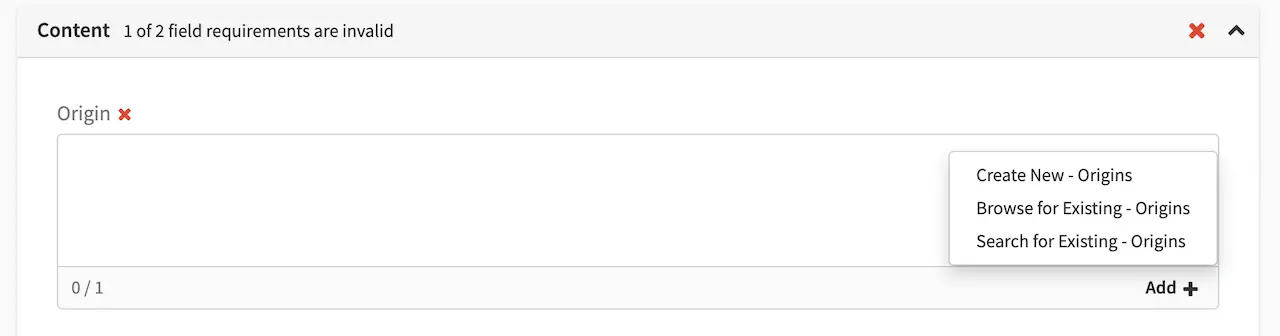
Let’s take a look at item specific dependencies in action for copying and deleting content. Let’s create a new article (Article content type) under one of the article folders in the Sidebar. Enter data in the required fields and remember to upload from desktop an image in the Image field in the Content section. Click on the Save & Close button. Note the location where the image is uploaded.

From the Sidebar, navigate to the newly created article. Right click on the article and select Copy. Navigate to a different folder, right click on the folder and select Paste.
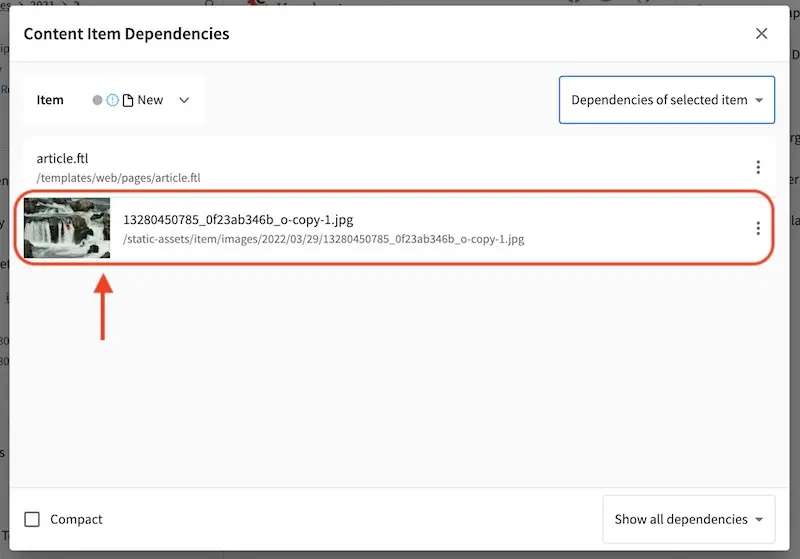
Let’s look at the dependencies of our copied article, where we expect a copy of the image under the /static-assets/item/images/2021/10/05 will be located since we have taken advantage of the item specific dependencies regex pattern of /static-assets/item/*.
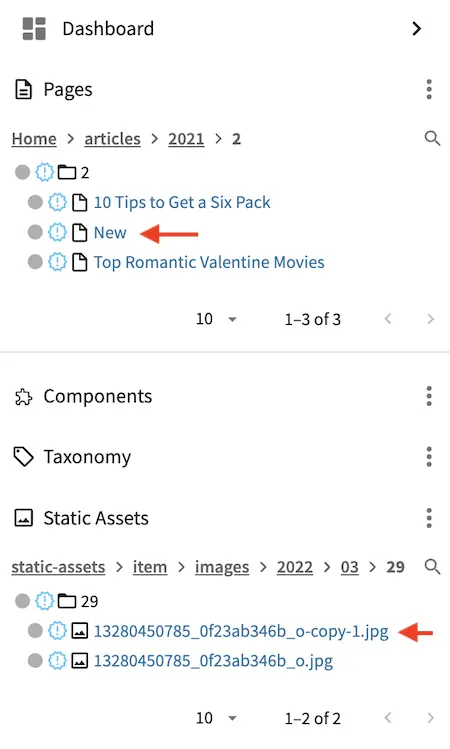
Let’s also take a look at the static-assets folder to see the copy of the uploaded image
Now let’s take a look at what happens when we delete content with item specific dependencies. From the Sidebar, navigate to the article that we created. Right click on the article and select Delete. Click on the Delete button when the Delete dialog appears. Notice the items that will be deleted when we delete the article.
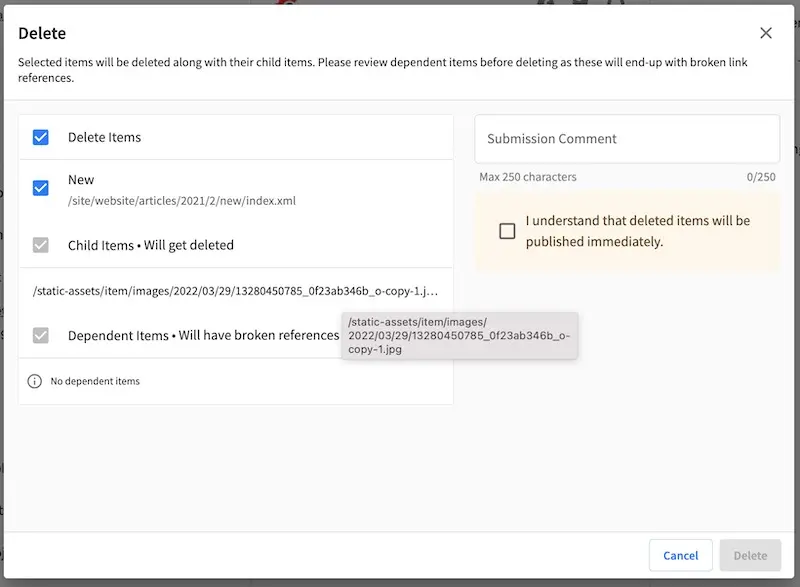
Open the Dashboard and notice the items that are deleted. We deleted an article, and since the image is located in a path matching the regex pattern for item specific dependencies, the image is deleted along with the article.
Quick Create
Quick create allows content authors to create content with as few clicks as possible through a button from the context nav for configured content types.

Let’s take a look at an example on how to configure a content type to be available from the quick create button in the context nav for authors using the out of the box blueprint Website Editorial. In the image below, we have a project named My Editorial with the quick create button expanded. Notice that we have one content type available for quick create, the Article content type.
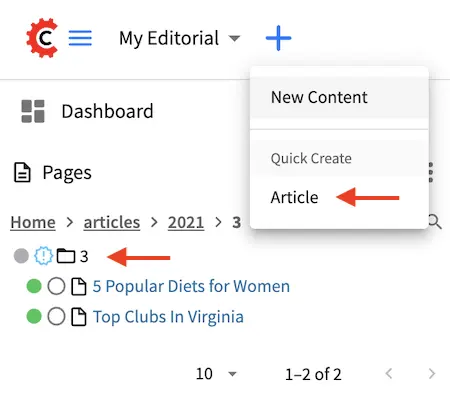
If you look at the project tree as shown above, most of the content (the articles) is organized in a dated folder structure. Adding quick create for the Article content type lets the content author skip having to open the Sidebar, then navigate through the project tree, create the year/month folder if it does not exist yet, then finally create their content.
To setup quick create for a content type, from the Sidebar, click on ![]() at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing. Next, go to the Properties Explorer and scroll to the Quick Create section of the properties.
at the bottom. Next, click on Content Types. We will select the content type Article for editing. Next, go to the Properties Explorer and scroll to the Quick Create section of the properties.
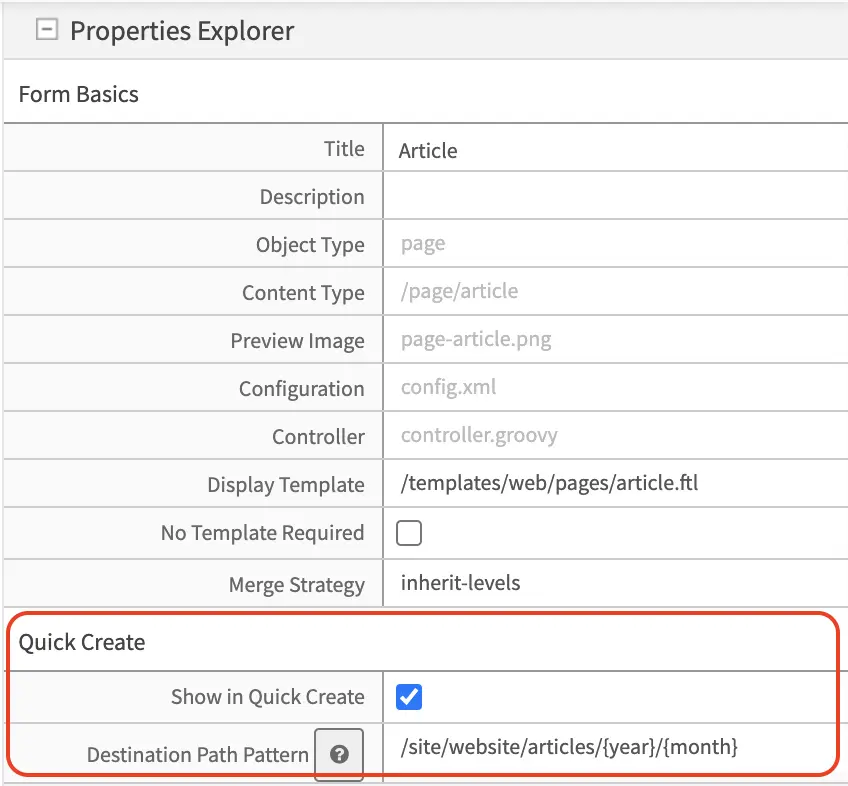
Check the Show in Quick Create property to make the content type available from the quick create button of the Article content type.
In the Destination Path Pattern, fill in the path pattern where the content created from quick create will be stored. For our example, notice that the articles are arranged in the following folder structure:
/articles
/{year}
/{month}
We will then put in /site/website/articles/{year}/{month} as the path pattern, which will put the new content into the year and month folder when the content author used quick create.
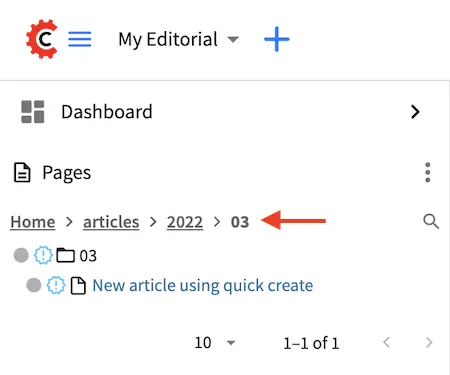
Below is the project tree after using the quick create button to create a new article titled New article using quick create, where the year and month folders were created for the new article using the value in the Destination Path Pattern property of the content type.
Form Controls
Form Controls are data input controls that, once placed on a form, will capture that input from the content authors and store it in the content object. CrafterCMS ships with a number of out-of-the-box controls and you can also create your own by reading Building Form Engine Control Project Plugins.
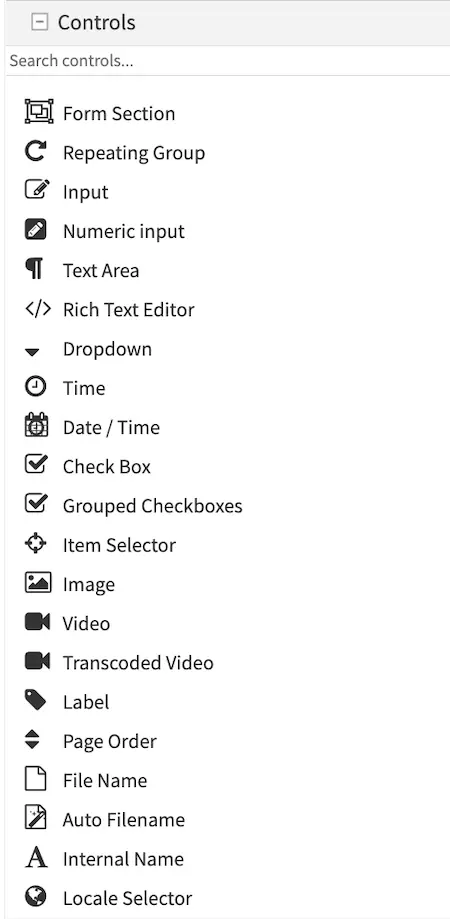
Each Form Control type has it’s own properties and constraints. Some constraints are common, like “Variable Name” and “Required” while others apply only to the type, e.g. Height and Width limitations on the Image Picker control.
Here’s a list of available Form Engine Controls:
Control
|
Description
|
 |
Create a new section in the form, this is to help the content
authors by segmenting a form into sections of similar concern.
Details are in the Form Section Control page.
|
 |
Repeating groups are used when the form has one or several controls
that repeat to capture the same data as records. For example: a
list of images in a carousel, or a list of widgets on a page.
Details are in the Repeating Group Control page.
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Transcoded Video selector from Video Transcoding Data Source.
Details are in the Transcoded Video Control page.
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Form Control Variable Names
Every Form Control has a Variable Name property. The Variable Name is used by the form engine to store the content entered by the user in the content model and search index. This same Variable Name is used later by templates and controllers to retrieve the value.
Variable Name Best Practices
Be descriptive. Well thought out Variable Names help with template and controller readability.
Use camel case. Example: “productSummary”.
Use regex constraints on input boxes to enforce additional validation rules
Do not use Reserved names.
Reserved Variable Names
The following variable names are used by CrafterCMS.
Variable Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
file-name*
|
Used by the File Name and Auto File Name control.
|
internal-name
|
Used by Crafter Studio to label the content object
|
placeInNav
|
Used by the Page Order control.
|
disabled
|
Used to logically remove an object in content delivery.
For more information, see Disabling a Page
|
expired
|
Used to logically remove an object after date
|
expired_dt
|
Used to logically remove an object after date
For more information, see Content Monitoring
|
objectId
|
UUID. Auto assigned by Crafter
|
objectGroupId
|
First part of objectId. Auto assigned by Crafter
|
createdDate
|
create date. Auto assigned by Crafter
|
createdDate_dt
|
Alternate name for create date. Auto assigned by Crafter
|
lastModifiedDate
|
Last modified date. Auto assigned by Crafter
|
lastModifiedDate_dt
|
Alternate name for last modified date. Auto assigned by Crafter
|
content-type
|
Content type name
|
display-template
|
Path to default template for type
|
merge-strategy
|
Crafter Core/Engine “Merge Strategy” for content type
|
id
|
reserved for a unique identifier
|
authorizedRoles
|
Used to restrict pages based on roles
|
role
|
Contains the role required to access a page
|
mime-type
|
Mime-type name
|
force-https
|
HTTPS connection needs to be forced to access the page
|
navLabel
|
Navigation label
|
redirect-url
|
Redirect URL
|
crafterSite
|
Used to set the site value
See note in Crafter Engine API for more information
|
localId
|
Name of the field for paths. Used by the deployer
|
rootId
|
Root Id name. Used by the deployer
|
includedDescriptors
|
Included descriptors field name. Used by the deployer
|
crafterPublishedDate
|
The name for the publish date field. Used by the deployer
|
disableFlattening
|
Used to indicate if XML flattening should be disabled when
indexing XML. Used by the deployer
|
content
|
Used by the deployer
|
contentType
|
Name of field for mimeType. Used by the deployer
|
width
|
Used by the deployer
|
height
|
Used by the deployer
|
contentLength
|
Name of field for file size. Used by the deployer
|
lastEditedOn
|
Name of field for last edit date. Used by the deployer
|
internalName
|
Name of field for internal name. Used by the deployer
|
* Note on file names
CrafterCMS supports the following characters in file and folder names:
Alphanumeric, ,_,-,(,)
as a regex:
[a-zA-Z0-9-_ ()]+
It’s important to point out that Crafter Studio enforces this regex in its UI. However, if you’re working outside of Studio (in your IDE, for example) and you violate these rules, problems may arise downstream, so it’s best to stick the allowed characters.
Note
A note on the
crafterSitereserved variable nameCrafter Engine and Crafter Studio identify which project a user is looking at by a number of different mechanisms with the following precedence:
Headers
QSA (Query String Parameters e.g.
crafterSite)Cookie
Additionally, if the cookie is not aligned, the cookie is to be reset to what’s above it.
Variable Names and Search Indexing
CrafterCMS indexes your content in the search index using your content model variable name as the field name.
To facilitate indexing, the following suffix should be appended to variable names depending on the variable data type:
Type
|
Field
Suffix
|
Multivalue
Suffix
(repeating
groups)
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|---|
integer
|
_i
|
_is
|
a 32 bit signed integer
|
string
|
_s
|
_ss
|
String (UTF-8 encoded string or Unicode). A string
value is indexed as a single unit.
|
long
|
_l
|
_ls
|
a 64 bit signed integer
|
text
|
_t
|
_txt
|
Multiple words or tokens
|
boolean
|
_b
|
_bs
|
true or false
|
float
|
_f
|
_fs
|
IEEE 32 bit floating point number
|
double
|
_d
|
_ds
|
IEEE 64 bit floating point number
|
date
|
_dt
|
_dts
|
A date in ISO 8601 date format
|
time
|
_to
|
_tos
|
A time in
HH:mm:ss format (the value will beset to date 1/1/1970 automatically)
|
text with
html tags
|
_html
|
Model fields require their respective data type postfix as listed above. The UI autofills the Name/ Variable Name field and adds postfixes as you’re typing in the Title field.
When setting up reserved variable names for your model, remember to remove the postfix auto-added by the UI since the variable name needs to be exactly the same as listed above.
Remember to also remove the postfix auto-added by the UI when using key or value for your variable names being setup as key-value pairs in a content type, such as the Taxonomy content type used in the Website Editorial blueprint.
Please note that indexed text fields are case insensitive when performing a search, while string fields are case sensitive. Also, queries using string fields will only match full values besides being case sensitive.
If performing a case insensitive search on a string field is desired, CrafterCMS provides a way by enabling tokenization of the field in the content type. To enable tokenization of a string field in Studio, put a check in the checkbox labeled Tokenize for Indexing in the properties section of the content type field. Below is the Article content type in a project created using the Website Editorial blueprint, showing the field Author with the Tokenize for Indexing option:
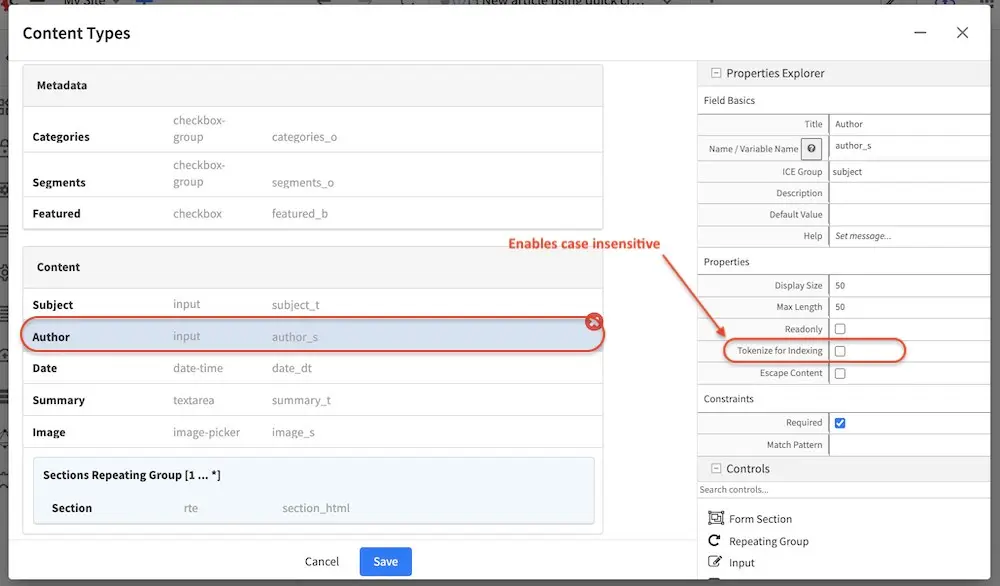
It should also be noted that when the tokenize option is enabled, a second field will be created with the _t postfix. This second field with the _t postfix should be used in queries to be case insensitive and match tokens. In our example above, the field author_t should be used in queries instead of author_s to be case insensitive and match tokens.
Let’s take a look at an example of queries performed on a string field with tokenize enabled and compare the results of using the field with the _s postfix and the second field created when we enabled tokenize with the _t postfix. We’ll use the Author field shown above with Tokenize for Indexing enabled. Here are the results of the queries using the author_s and author_t fields:
Query |
Matches author_s? |
Matches author_t? |
|---|---|---|
Jane |
No |
Yes |
jane |
No |
Yes |
Jane Doe |
Yes |
Yes |
jane doe |
No |
Yes |
Jane doe |
No |
Yes |
Another thing to note is since CrafterCMS stores content as XML files, certain content fields which contain special characters must be escaped. By default, CrafterCMS will escape content fields of types:
HTML (_html)
Text (_t)
String (_s)
Multi-valued string (_smv, _mvs)
Internal-name (internal-name)
This default configuration can be modified by editing the element <cdata-escaped-field-patterns> in the configuration file Project Configuration from the Project Tools -> Configuration
1<!--
2 Specifies the regular expression patterns to match content type field
3 names that require CDATA escaping.
4-->
5<cdata-escaped-field-patterns>
6 <pattern>(_html|_t|_s|_smv|mvs)$</pattern>
7 <pattern>internal-name</pattern>
8</cdata-escaped-field-patterns>
Data Sources
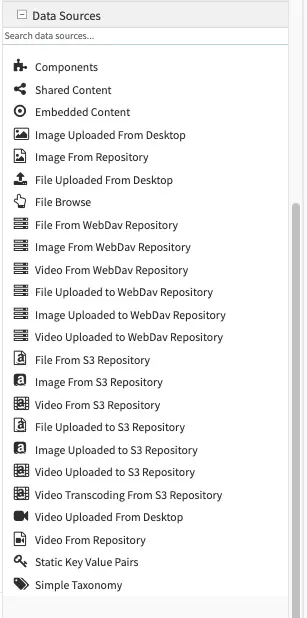
Data Sources are pickers that help pull in content from internal or external storage/systems. For example, data source include: desktop video uploader, desktop image uploader, and so on. CrafterCMS ships with a number of out-of-the-box data sources and you can also create your own by reading Building Form Engine Data Source Project Plugins.
Data Sources allows the content model designer to decide where different assets uploaded via different controls go (for instance icons, images, RTE related assets, etc.). It has it’s own properties, like “Repository Path”, which specifies the path where assets are stored, which help keep the system consistent over time. The storage destination designed in the model dictates how those assets are handled during a duplicate event (duplicate the asset or duplicate the reference to the asset).
List of Data Sources
Form Engine Data Sources (please use the scrollbar to see more data sources)
Macros for Data Sources
There are a number of macros available for the content model designer to use in data sources. These macros are used when uploading assets to better organize project items, usually in the Repository Path property of the data source for uploading. Here are the available macros:
Macro
|
Description
|
|---|---|
{objectId}
|
Inserts a GUID
|
{objectGroupId}
|
Inserts the first 4 characters of a GUID
|
{objectGroupId2}
|
Inserts the first 2 characters of a GUID
|
{year}
|
Inserts the current year (4 digit year)
|
{month}
|
Inserts the current month (2-digit month of the year)
|
{parentPath}
|
Inserts the parent path of the component/page containing the upload controls
|
{parentPath[index]}
|
Inserts the sub element of a parent path using an index, of the component/page
containing the upload controls
|
{yyyy}
|
Inserts the current year (4 digit year)
|
{mm}
|
Inserts the current month (2-digit month of the year)
|
{dd}
|
Inserts the current day (2-digit day of the month)
|
For an example of how the macros are used when modeling your content, the website_editorial blueprint uses some of the macros available in the content type Article.
The section Item Specific Dependencies above details the use of some of the macros in the website_editorial blueprint, content type Article.
Note
For both the
parentPathandparentPath[index]macros, the path starts without/site/websiteand/site/components.For example, if in the repository the parent is a page, and the page URL in the repository is
/site/website/en/about-us/index.xml, then the parentPath is/en/about-us/index.xml.If in the repository the parent is a component, and the component URL in the repository is
/site/components/en/products/myproduct.xml, then the parentPath is/en/products/myproduct.xml.
Data Sources macro: parentPath[index]
The parentPath[index] macro provides resolution support for sub elements of a parent path in Crafter Studio.
It pulls a single sub / of the parent path with the following syntax {parentpath[index]}
Here are some examples:
If the parentPath is /en/mypage, then to get the sub element en, use 0 as the index in the macro like so {parentpath[0]}
If the parentPath is /products/household/cleaning then to get the sub element household, use 1 as the index in the macro like so {parentpath[1]}
Form Canvas
The canvas is where the form actually gets built. The building process is performed by simply dragging the controls from the Form Controls over to the canvas, rearranging the controls in the order you’d like to present to the content authors, and configuring the controls individually.
Controls on the canvas are configured by clicking on the control, and then editing the control’s configuration in the Properties Explorer, see item #3 in Form Builder Basics. Different controls have different configuration, so please review the individual form control configuration listed in Form Controls.
Two controls have a special significance to the form canvas: Form Section Control and Repeating Group Control. Form Section Control creates a form section that can be expanded and collapsed and holds within it other controls. This is typically used to group together controls that cover a similar concern and help provide the content authors with a clear and organized form when editing in form mode. Like the Form Section Control, Repeating Group Control is also a container that holds other controls, but the purpose is to allow a set of controls to repeat as configured. This is typically used to allow content authors to enter a set of meta-data and repeat it as many times as desired and permitted by configuration.
The canvas allows the form-based content capture only, and is used by content authors when they’re in that mode. In-Context Editing will leverage the form components, but not the canvas when authors are in that mode. Learn more about In-Context Editing configuration in Experience Builder.
Content Type View Templates
View templates control how the model is rendered as HTML. Crafter uses FreeMarker as the templating engine, and provide the full model defined by the model in the previous section. Every element in the model is accessible to the view template via a simple API ${contentModel.VARIABLE_NAME} where variable name is the Name / Variable Name definition in the Form Control. View templates are primarily written in HTML, backed by CSS with API calls weaved within to pull content from the primary CrafterCMS model or additional model (via APIs, please read Groovy API for that topic).
An example view template
1<#import "/templates/system/common/cstudio-support.ftl" as studio />
2
3<!DOCTYPE html>
4<html lang="en">
5 <head>
6 <!-- Basic Page Need
7 ================================================== -->
8 <meta charset="utf-8">
9 <title>${contentModel.browser_title}</title>
10 <meta name="description" content="${contentModel.meta_description}">
11 <meta name="keywords" content="${contentModel.meta_keywords}">
12 </head>
13 <body>
14 <div class="body" <@studio.iceAttr iceGroup="body"/>>
15 ${contentModel.body_html}
16 </div>
17
18 <#if (contentModel.analytics_script)??>${contentModel.analytics_script}</#if>
19 </body>
20</html>
The simple example renders a simple HTML page with a very basic model. Let’s review the model first:
Model Element
|
Control
|
Purpose
|
browser_title
|
Input
|
Provide a browser title for the page
|
meta_keywords
|
Input
|
SEO keywords associated with the page
|
body_html
|
Rich Text
Editor
|
The page’s main HTML body (in this case, it’s
just a static HTML block).
|
analytics_script
|
Text Area
|
Analytics’s Engine JavaScript
|
The FreeMarker language is supported. For detailed Freemarker documentation, please visit: http://freemarker.org
Content Type Controller Definition
Crafter page and components can have their own controller scripts too, that are executed before the page or component
is rendered, and that can contribute to the model of the template. These scripts, besides the common variables, have
the templateModel and the contentModel available. The templateModel is the actual map model of the
template, and any variable put in it will be accessible directly in the template, eg. if the script has the line
templateModel.var = 5, then in the template the var’s value can be printed with ${var}. The contentModel
is the XML descriptor content, of type SiteItem. The scripts don’t have to return any result, just populate the
templateModel.
There are 2 ways in which you can “bind” a script to a page or component:
Put the script under Scripts > pages or Scripts > components, and name it after the page or component content type.
When creating the content type for the page or component, add an Item Selector with the variable name
scripts. Later when creating a page or component of that type, you can select multiple scripts that will be associated to the page or component.
The following is an example of a component script. The component content type is /component/upcoming-events. We can then place the
script in Scripts > components > upcoming-events.groovy so that it is executed for all components of that type.
1import org.craftercms.engine.service.context.SiteContext
2
3import utils.DateUtils
4
5def now = DateUtils.formatDateAsIso(new Date())
6def queryStr = "crafterSite:\"${siteContext.siteName}\" AND content-type:\"/component/event\" AND disabled:\"false\" AND date_dt:[${now} TO *]"
7def start = 0
8def rows = 1000
9def sort = "date_dt asc"
10def query = searchService.createQuery()
11
12query.setQuery(queryStr)
13query.setStart(start)
14query.setRows(rows)
15query.addParam("sort", sort)
16query.addParam("fl", "localId")
17
18def events = []
19def searchResults = searchService.search(query)
20if (searchResults.response) {
21 searchResults.response.documents.each {
22 def event = [:]
23 def item = siteItemService.getSiteItem(it.localId)
24
25 event.image = item.image.text
26 event.title = item.title_s.text
27 event.date = DateUtils.parseModelValue(item.date_dt.text)
28 event.summary = item.summary_html.text
29
30 events.add(event)
31 }
32}
33
34templateModel.events = events
You might notice that we’re importing a utils.DateUtils class. This class is not part of CrafterCMS, but instead it is a Groovy class
specific to the project. To be able to use this class, you should place it under scripts > classes and name it DateUtils.groovy,
where everything after the groovy directory is part of the class’ package. It’s recommended for all Groovy classes to follow this
convention.
1package utils
2
3import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
4
5class DateUtils {
6
7 static def parseModelValue(value){
8 def dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss")
9 dateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"))
10 return dateFormat.parse(value)
11 }
12
13 static def formatDateAsIso(date) {
14 def dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss'Z'")
15 dateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"))
16 return dateFormat.format(date)
17 }
18}
For more information on the FreeMarker (Templating) APIs, please see FreeMarker (Templating) API.
For more information on the Groovy APIs, please see Groovy API
Note
Scripts and Templates Security
Crafter Engine limits access to services when developing templates or scripts, and sandboxes scripts for security by default.
Crafter Engine only allows a small list of services available to use when developing templates or scripts. There are some sites that may require services not included by default.
To expose other services, follow the guide Access to Services
Scripts are executed in a sandbox that has a blacklist of insecure expressions to prevent code that could compromise the system. There are some cases though where a site requires access to one or more of the blacklisted expressions.
To override the default script sandbox configuration, follow the guide Script Sandbox Configuration